Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250218-54
- Publication
- He et al., 2025 - Gallbladder-derived retinoic acid signalling drives reconstruction of the damaged intrahepatic biliary ducts
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
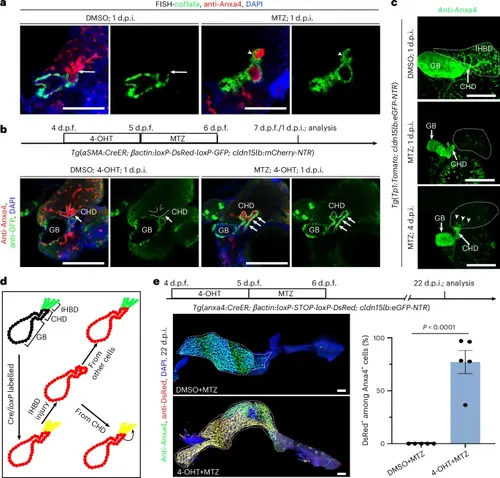
IHBD damage induces migration of the gallbladder smooth muscle to coat the CHD and subsequent ingrowth of the CHD into the inner liver in zebrafish.a, FISH combined with antibody staining images of col1a1a and Anxa4 at 1 d.p.i. The CHD was enwrapped by col1a1a+ muscle cells within 1 d.p.i. in response to IHBD damage (n = 13/13; arrowhead) compared to the DMSO group (n = 10/10; arrow). b, Experimental strategies for lineage tracing of SMCs, and antibody staining images of GFP and Anxa4 at 1 d.p.i. in DMSO-treated (n = 5/5) and MTZ-treated (n = 8/10) groups with 4-OHT incubation. c, Confocal projection and antibody staining images of Anxa4+ biliary trees in DMSO-treated (n = 8/8) and MTZ-treated zebrafish at 1 d.p.i. (n = 14/14) and 4 d.p.i. (n = 12/16). Note that newly regenerating IHBD cells start from the CHD at the early regeneration stage. d, Experimental strategies for lineage tracing of new regenerating IHBD cells. e, Top: experimental strategies for lineage tracing. Left: confocal projection and antibody staining images of Anxa4 and DsRed in DMSO- and 4-OHT-treated zebrafish at 22 d.p.i. Right: quantification of the ratio of DsRed+ among Anxa4+ IHBD cells in DMSO-treated (n = 5 zebrafish) and 4-OHT-treated (n = 5 zebrafish) zebrafish. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m.; unpaired t-test. Scale bars, 100 μm. |