Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240605-35
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2023 - Selenium deficiency-induced high concentration of ROS restricts hypertrophic growth of skeletal muscle in juvenile zebrafish by suppressing TORC1-mediated protein synthesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
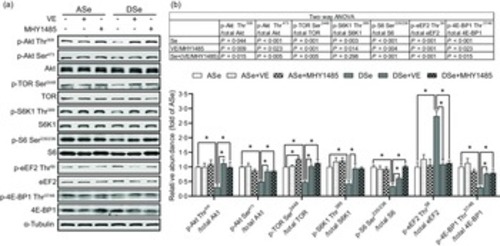
Effects of 30 d of dietary treatments on Akt-TORC1 pathway in skeletal muscle of juvenile zebrafish. Data were obtained 2 h after a meal by (a) Western blotting assay, and (b) the relative phosphorylation levels of proteins in Akt-TORC1 pathway were calculated. Values are means ± SEM, n 3. *Significantly different (P < 0·05, two-way (dietary Se × dietary VE or MHY1485) ANOVA followed by Bonferroni–Dunn multiple comparison). ASe, the basal Se-adequate diet; DSe, the basal Se-deficient diet; VE, DL-α-tocopherol acetate, antioxidant; MHY1485, activator of the target of rapamycin; Akt, protein kinase B; TOR, the target of rapamycin; TORC1, the target of rapamycin complex 1; S6K1, 70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase; S6, ribosomal protein S6; eEF2, eukaryotic translation elongation factor 2; 4E-BP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein. |