Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240307-14
- Publication
- Russell et al., 2021 - Pathogenic effect of TP73 Gene Variants in People With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
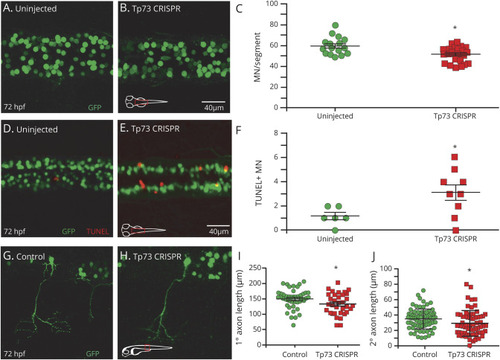
tp73 Mutation Decreases Motor Neuron Count, Increases Apoptosis, and Impairs Motor Neuron Axon Outgrowth (A and B) Confocal images of spinal motor neurons (MNs; green) in uninjected and tp73CRISPR injected embryos (confocal imaging of dorsal view of spinal cord). (C) tp73CRISPR-injected embryos have a significantly reduced number of MNs compared to both uninjected and tyrCRISPR-injected sibling controls (supplement figure 4, C and D, doi:10.5061/dryad.4qrfj6q94). (D and E) Confocal images of increased MN (green) apoptosis (red terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling [TUNEL]) in tp73CRISPR embryos compared to uninjected. (F) Increased MN apoptosis in tp73CRISPR embryos compared to uninjected, performed in mnx:GFP transgenic line. (G and H) Confocal images of MN primary and secondary axons (green) in uninjected and tp73CRISPR-injected embryos. (I) MN primary axon length in tp73CRISPR embryos is significantly shorter than that of uninjected sibling controls. (J) MN secondary axon length in tp73CRISPR-injected embryos is significantly shorter compared to that of uninjected sibling controls. CRISPER = clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; hpf = high-power field. |