Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240109-84
- Publication
- Ma et al., 2023 - Hypoxia tolerance in fish depends on catabolic preference between lipids and carbohydrates
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
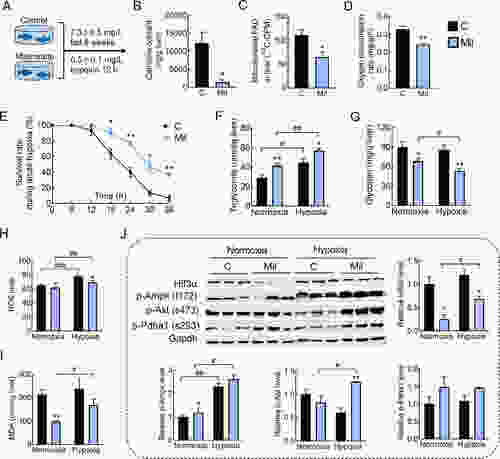
Effects of biochemical lipid catabolism inhibition on tolerance to acute hypoxia in Nile tilapia A: Nile tilapia were fed control (C) or mildronate (Mil) diets for six weeks and sampled under normoxic and hypoxic conditions after 12 h. B: L-carnitine (Car) content in liver. C: Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in liver. D: Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in Nile tilapia. E: Survival rate of Nile tilapia during acute hypoxia. F: Triglyceride (TG) content in liver. G: Glycogen content in liver. H: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) content in liver. I: Malondialdehyde (MDA) content in liver. J: Protein expression of Hif3α, p-Ampk (t172), p-Akt (s473), p-Pdha1 (s293), and Gapdh in liver. |