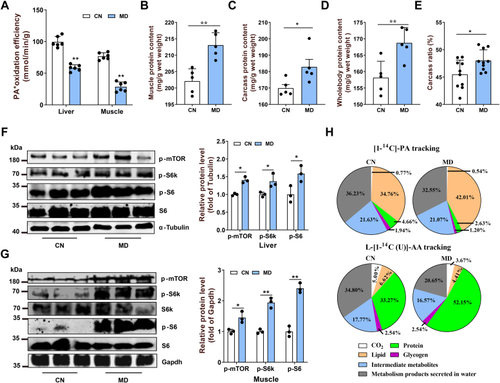
Mitochondrial FAO inhibition activates the mTORC1 pathway and increases protein synthesis in zebrafish.A, isotope tracer analysis (PA∗, [1–14C] palmitic acid) to assess mitochondrial FAO efficiency in liver and muscle tissues. N = 6. B–E, the effects of mitochondrial FAO inhibition by mildronate (MD) on muscle protein content (B, n = 5), carcass protein content (C, n = 5), whole body protein content (D, n = 5), and carcass ratio (CR) (E, n = 9) in zebrafish. CR = 100 × (carcass weight/body weight). The carcass is mainly muscle tissue. F and G, the mTORC1 activity in liver (F) and muscle (G) tissues was detected by Western blotting for key proteins of the mTORC1 pathway. p indicates phosphorylated protein. Liver and muscle tissues were lysed, and Western blots for p-mTORSer2448, p-S6kThr389, S6k, p-S6Ser235/236, and S6 are shown. N = 3. H, metabolic tracking of [1–14C]-PA and l-[14C (U)]-AA in zebrafish-fed CN and MD diets for 6 weeks (H). N = 6. Data represent mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01. AA, amino acid; CN, control; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.
|

