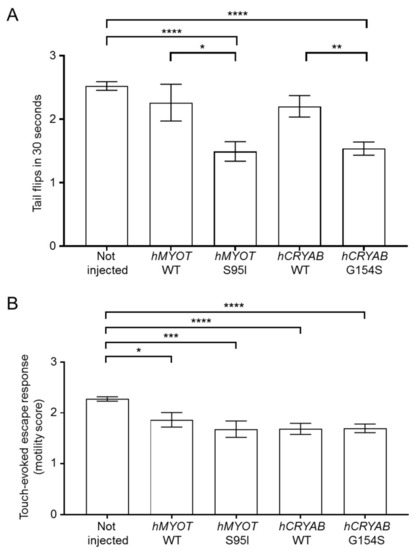
Effects on zebrafish motor behavior of both wildtype and mutant hMYOT and hCRYAB genes. (A). Tail flips. Spontaneous coiling events (tail flips) performed by wildtype zebrafish (not injected or injected with 25 µM of tol2 expression plasmid harboring hMYOT WT, hMYOT S95I, hCRYAB WT, hCRYAB G154S cDNA sequences) were recorded at 24 hpf. Graph bars represent the media of tail flips performed by each embryo in 30 s ± s.e.m. (B). Touch-evoked escape response was measured at 48 hpf on the same embryos reported in (A). A value of 0 was attributed to completely paralyzed embryos, 1 to embryos performing only spontaneous coiling events, 2 to embryos moving short distances, and 3 to embryos swimming normally. Graph bars represent the media of motor value for each condition ± s.e.m. Values in (A,B) represent the media from 4 independent experiments. Number of embryos analyzed for (A): not injected (n = 330), hMYOT WT (n = 50), hMYOT S95I (n = 59), hCRYAB WT (n = 109), hCRYAB G154S (n = 168). Number of embryos analyzed in (B): not injected (n = 342), hMYOT WT (n = 66), hMYOT S95I (n = 50), hCRYAB WT (n = 108), hCRYAB G154S (n = 148). p values were calculated by using One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
|

