Figure 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230501-157
- Publication
- Pose-Méndez et al., 2023 - Lifelong regeneration of cerebellar Purkinje cells after induced cell ablation in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
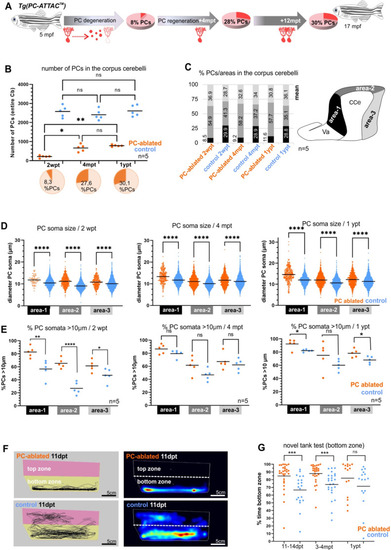
(A) Illustration of the percentage of PC layer replenishment during degeneration and regeneration phases. (B) Number and percentage of PCs after induced PC ablation monitored until 1 ypt. (C) Subdivision of the corpus cerebelli (CCe) into rostral, dorsal and caudal areas (areas 1–3), and the respective proportion of PCs in each area. (D) Quantification of the diameter of PC somata in the different areas of the CCe. (E) Percentage of PCs with somata larger than 10 µm from the total amount of PCs per area per brain. (F) Representative images of swim tracks and heat map of location of adult zebrafish in the novel tank test during 6 min. (G) Percentage of time spent in the bottom zone. The data correspond to the results from three independent PC ablations that were pooled. The cellular quantification in all graphs represent PCs from the entire CCe of 5 fishes per group per time point, as average from the whole PC population of each brain (B, C, E), or at single-cell level that were pooled (D). Statistical information: statistical method=analysis of variance (ANOVA) test for multiple groups comparison (ordinary one-way ANOVA- followed by Sidàks multiple comparison test), or Student’s t-test for two groups comparison (unpaired t-test two tailed for parametric, or Mann-–Whitney two tailed for no parametric data), levels of significance=P<0.05 (*), P<0.01 (**), P<0.001 (***), P<0.0001 (****). Additional information in Supplementary file 1.
|