Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221209-18
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2021 - Dissecting VEGF-induced acute versus chronic vascular hyperpermeability: Essential roles of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
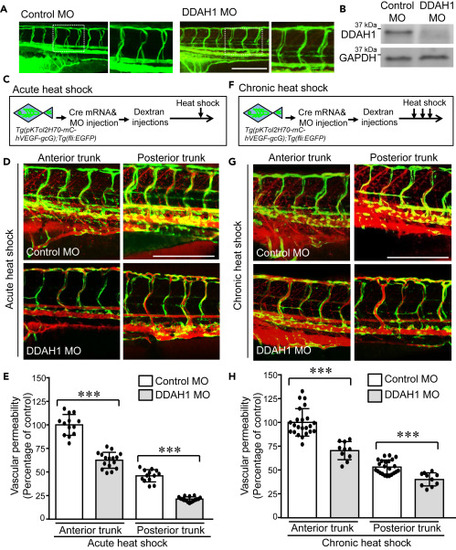
Figure 4. Knockdown of DDAH1 reduces VEGF-mediated acute and chronic vascular hyperpermeability Double transgenic zebrafish Tg(pKTol2H70-mC-hVEGF-gcG);Tg(fli:EGFP) were injected with Cre mRNA and DDAH1 or control morpholino (100 μM, 4.5 nL) at one-cell stage and then microinjected Texas Red-dextran (70 kDa) to the pericardium at 3-dpf. (A) Alignment of ISVs was analyzed. (B) Zebrafish embryos were collected and subjected to western blotting to confirm the decrease of DDAH1 protein levels. (C–F) Control and DDAH MO-injected zebrafish embryos were exposed to a single stimulus of heat shock at 37°C for 30 min (C and D) and three times of incubation at 37°C for 30 min separated by 30-min intervals at 28.5°C (F–G). Zebrafish embryos were imaged (D, G) and the vascular permeability of anterior and posterior trunk regions were quantified with our algorithm and compared (E and H). ∗∗∗, p < 0.001. Zebrafish numbers in each group are presented in the scatter plot. Data is expressed as mean ± SD. Scale bar, 200 μm, in (A, D, and G). |