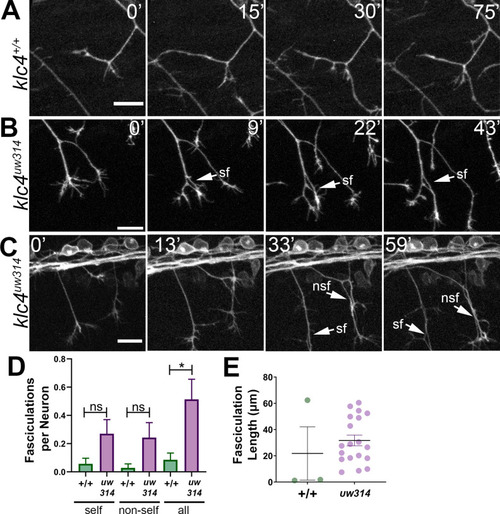
(A) In wild type embryos, the most common response to self or non-self contact between axons is retraction. Two neighboring axons in a wild type embryo make contact (time 0’) and within 30 min, one of the axons has retracted. (B–C) When axons make contact in klc4uw314 embryos, they often fasciculate instead of retracting. This happens with both self-contacts (B–C, sf) and non-self-contacts (C), nsf. All scale bars = 20 µm. (D) Fasciculations per neuron, separated by self or non-self, as well as all fasciculations combined. Wild type N=35 neurons in 4 embryos. Klc4uw314 N=37 neurons in 5 embryos. Error bars = SEM. (E) Fasciculation length was measured from the last frame of each 2 hr imaging period. Wild type N=3 fasciculations, klc4uw314 N=19 fasciculations. Mean with SEM displayed over individual data points. Because fasciculation events are rare in wild-type embryos and a length measurement is conditional on the event occurring, we could not apply a statistical test to assess the significance of the difference in fasciculation length.