Figure 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221020-18
- Publication
- Revathidevi et al., 2022 - AMBRA1 p.Gln30Arg Mutation, Identified in a Cowden Syndrome Family, Exhibits Hyperproliferative Potential in hTERT-RPE1 Cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
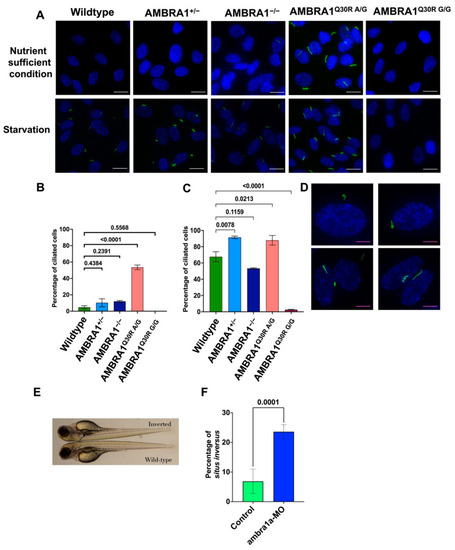
AMBRA1 Q30R mutant hTERT-RPE1 cells exhibited abnormal primary ciliogenesis. (A) Immunocytochemistry images of cells stained with Arl13B (ADP Ribosylation Factor Like GTPase 13B), a primary cilia marker (stained green), and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), a nucleus marker (stained blue). White scale bar = 25 μm (B) Bar graph representing the percentage of ciliated cells in each AMBRA1 genotype in nutrient-sufficient condition. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA. (C) Bar graph representing the percentage of ciliated cells in each AMBRA1 genotype under starvation. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA. (D) Representative immunocytochemistry images of AMBRA1Q30R A/G mutant cells stained with Arl13B and DAPI, showing abnormal ciliary structures (curled—top; double cilia—bottom left; spiral—bottom right). Magenta scale bar = 15 μm (E) ambra1a zebrafish CRISPANT showing a situs inversus phenotype. The arrow indicates the reverse orientation of the gall bladder in ambra1a knockout zebrafish (top) and its normal orientation in wildtype zebrafish (bottom). (F) Bar graph representing the percentage of zebrafish showing situs inversus phenotype. Statistical significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |