Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220328-8
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2021 - Biallelic variants in KARS1 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders and hearing loss recapitulated by the knockout zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
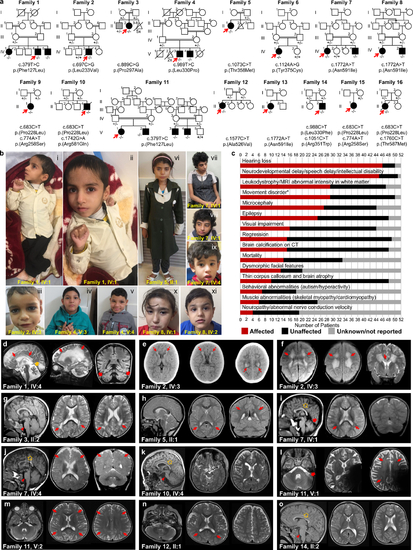
Fig. 1. Identification of pathogenic variants in KARS1 in 16 families and clinical summary. (a) Pedigrees and segregation data for the 16 families included in this study. Affected and unaffected individuals are indicated by filled and open squares (males) and circles (females), respectively. Probands are marked with red arrows. Double lines indicate consanguinity. Genetic diagnoses were made in 22 individuals. (b) Clinical characteristics of patients with homozygous KARS1 variants, including affected individuals from family 1 (IV:4) (i, ii), family 2 (IV:3) (iii), family 4 (V:3) (iv) and (V:4) (v), family 5 (II:1) (vi), family 7 (IV:1) (vii, viii) and IV:4 (ix), and family 8 (IV:1) (x) (IV:2) (xi). Frequent clinical features include: spasticity and contractures in the limbs with clenched hands (i, ii), high forehead (iv, v, vi, vii, x), prominent nose (i, ii, iv, v, vi, vii, viii), low-set ears (i, ii, iv, v, vii, viii, ix), and short philtrum (i, ii, iv, v, vi, vii, ix, x). (c) Phenotype summary of features associated with KARS1 pathogenic variants. Asterisk denotes movement disorders that include ataxia, spasticity, quadriplegia, dystonia, or chorea/tremor. (d–o) Neuroimaging features associated with KARS1 variants, with variable patterns of white matter (WM) involvement (red arrows), calcifications (red dotted arrows), pontine hypoplasia (red arrowheads), cerebellar atrophy (red thick arrows), enlargement of the cerebral cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) spaces, and corpus callosum hypoplasia (gold arrows). |