FIGURE 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210402-3
- Publication
- Montgomery et al., 2021 - Repetitive optogenetic stimulation of glutamatergic neurons: An alternative to NMDA treatment for generating locomotor activity in spinalized zebrafish larvae
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
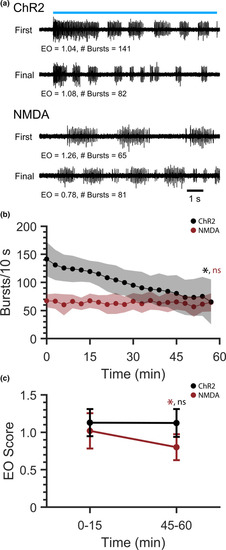
Comparison of robustness and organization of repetitive ChR2‐induced and continuous NMDA‐induced fictive swimming. ChR2‐induced and NMDA‐induced fictive swimming were recorded from spinalized |