Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210323-14
- Publication
- Ka et al., 2021 - Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Dyslipidemia and Associated Diseases
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
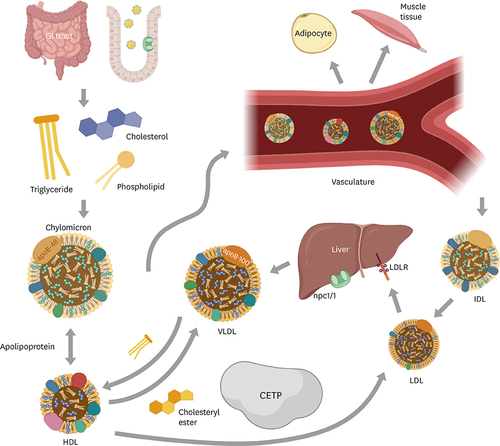
Lipid ingestion and metabolism. Lipids from foods are digested in GI tract. Ingested lipids are hydrolyzed into small, absorbable molecules such as fatty acids and monoglycerides and products by lipolysis are subsequently re-esterified into TGs in the enterocytes. Cholesterol is absorbed through the transport protein npc1l1, a critical mediator of cholesterol absorption. TGs with cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins, cholesteryl ester and phospholipids forms chylomicrons in the intestine. Chylomicron acquires apolipoproteins from HDLs in vasculature. VLDLs are synthesized in liver, and they possess apoB-100, in contrast, chylomicrons possess apoB-48, although both deliver TGs to peripheral tissue. LDLs, converted particles from IDLs, are cleared in liver via LDL receptors. CETP mediates exchange of cholesteryl ester and TGs between VLDLs, LDLs and HDLs. GI, gastrointestinal; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; apo, apolipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; IDL, intermediate density lipoprotein; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein. |