Figure 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210307-76
- Publication
- Campbell et al., 2020 - PTPN21/Pez Is a Novel and Evolutionarily Conserved Key Regulator of Inflammation In Vivo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
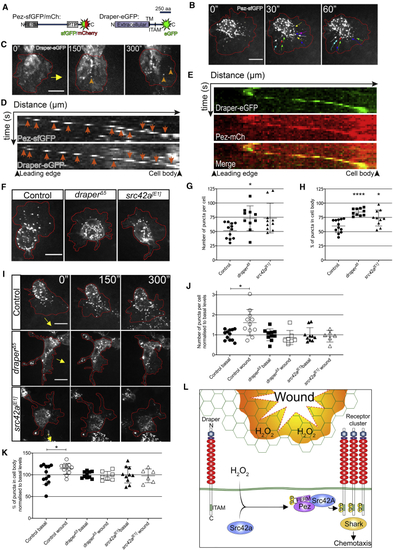
Dynamic Pez Puncta Are Stimulated upon Wounding in a Draper-Dependent Manner (A) Diagrams of fluorescently tagged Pez and Draper constructs. For Pez, the FERM and PTP domains are shown. For Draper, the N-terminal extracellular domain is noted, along with the transmembrane domain (TM) and immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM). (B) Pez forms puncta within the cell body and lamellipod. Dynamic lamellipodial puncta flow inward from the cell periphery (denoted by red line). Colored arrows show puncta tracking over 1 min. (C) Dynamic Draper-EGFP puncta (orange arrowheads) induced post-wounding. Red line donates cell periphery; yellow arrow indicates direction of wound. (D) Kymographs of individual Pez-sfGFP and Draper-EGFP puncta (orange arrows) following wounding demonstrate similar dynamics over time. (E) Kymograph of Draper-EGFP punctum reveals colocalization with Pez-mCh following wounding. For all kymographs, the x axes represent distance starting at lamellipod leading edge (174 nm/pixel; 17.4 μm total). The y axes represent time (10 s/pixel; 2.5 min total). (F) Lamellipodial Pez-sfGFP puncta are suppressed in (G and H) Puncta number (G) and distribution (cell body versus lamellipod; H) significantly altered in mutants (n ≥ 10 cells from ≥5 embryos/genotype; Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons, respectively). (I) Images of control, (J and K) Analysis of Pez puncta 5 min post-wounding reveals (J) a wound-induced significant increase in puncta number that is dependent on both Draper and Src42A (n ≥ 6 cells from ≥5 embryos/genotype for each condition; Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons) and (K) a wound-induced significant increase in the proportion of puncta residing within the cell body of control cells that is absent in (L) Proposed role of Pez in wound-induced Draper clustering. Under basal conditions, Draper’s ITAM domain remains in an inactive state. Following H2O2-mediated Src42A activation, phosphorylated Pez is recruited to Draper clusters via its FERM-domain-mediated interaction with Src42a. Acting as an adaptor, Pez coordinates inflammatory Draper signaling via effectors such as Shark, leading to efficient macrophage chemotaxis. See also |