Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-201210-8
- Publication
- Everson et al., 2020 - Multifactorial Genetic and Environmental Hedgehog Pathway Disruption Sensitizes Embryos to Alcohol-Induced Craniofacial Defects
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
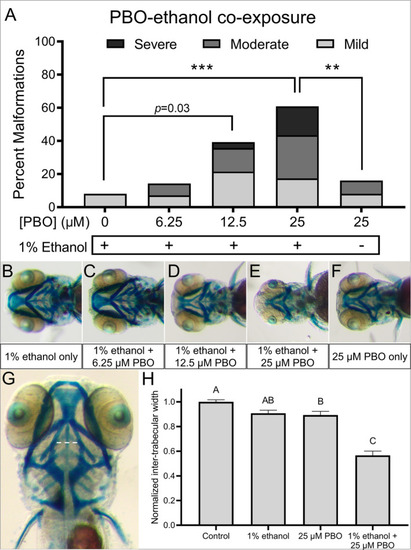
Ethanol and PBO synergistically interact to cause craniofacial defects. ( |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Conditions: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |