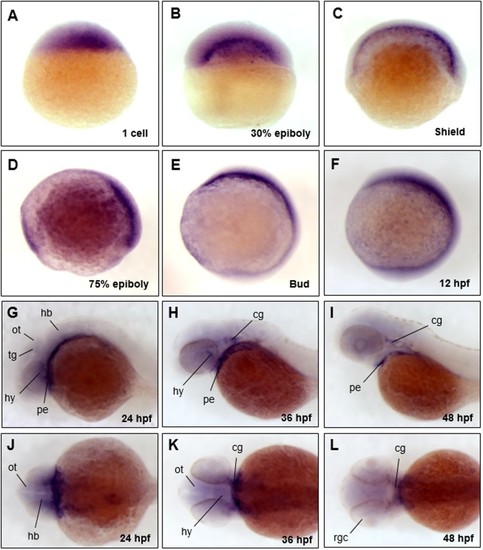
The spatio-temporal expression patterns of trim45 in early embryonic stages of zebrafish. Whole mount in situ hybridization (WISH) was performed using digoxygenin-labeled trim45 RNA probe at one cell, 30% epiboly, shield, 75% epiboly, bud, 12, 24, 36, 48 hpf stages. trim45 had maternal messages from one cell stage (A). From 30% epiboly stage (B) to shield stage (C), expression was restricted to the yolk syncytial layer (YSL). At 75% epiboly (D), trim45 was mainly expressed in dorsal mesoderm. At bud and 12 hpf stage (E and F), trim45 was strongly expressed in the head region of the anterior pole. At 24 hpf stage, trim45 was expressed in pharyngeal endoderm, tegmentum, optic tectum, and hindbrain (G and J). At 36 hpf stage, trim45 was expressed in hypothalamus, pharyngeal endoderm, and cranial ganglion (H and K). At 48 hpf stage, trim45 was expressed in pharyngeal endoderm, cranial ganglion, and retinal ganglion cell layer (I and L). Embryo orientations: lateral views (A–I) and dorsal views (J–L). Black lines point to various anatomical structures. pe, pharyngeal endoderm; ot, optic tectum; tg, tegmentum; te, telencephalon; mb, midbrain; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; rgc, retinal ganglion cell layer; cg, cranial ganglion.
|

