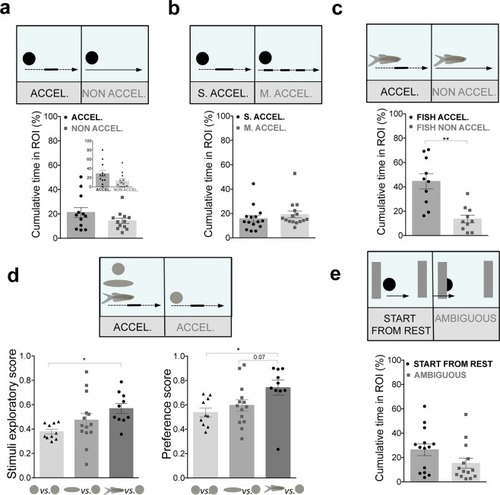
Zebrafish perceives elementary cues of biological motion and shape enhances this preference. (a) Zebrafish preference towards speed-changes (acceleration) cues. % Cumulative time fish spent next to a dot with speed-changes cues (ACCEL., black dot) vs. constant mean speed cue (NON ACCEL., grey squares) (n = 12). Depict of the % cumulative time in ROI during the first 2 min of the trial is shown. (b) Increasing the moments of acceleration do not increase preference towards speed-changes. % Cumulative time fish spent next to a single speed change (S.ACCEL., black dots) vs. multiple speed-changes (M. ACCEL., grey squares, n = 15). (c) Conspecific shape enhances attraction to speed-change cues. % Cumulative time fish spent next to a fish image with speed-changes (FISH ACCEL., black dots) vs. constant speed (FISH NON ACCEL., grey squares, n = 10). (d) Shape enhances attraction to acceleration cues. Changing from dot to elongated shape, and to conspecific form increases stimuli exploratory score and preference score. (e) Zebrafish preference towards start from rest cues. % Cumulative time fish spent next to a start from rest stimulus (START FROM REST, black dots) vs. an ambiguous stimulus (grey squares, n = 14). Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
|

