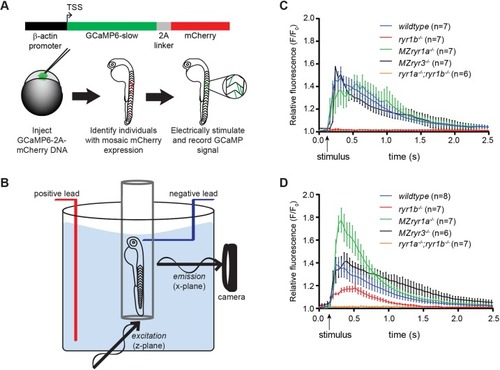
Muscle fiber type-specific roles of RyR channels. (A) Schematic for generating zebrafish embryos that mosaically express GCaMP in muscle fibers. One-cell stage embryos were injected with a DNA expression plasmid driving constitutive expression from the B-actin promoter of GCaMP6-slow translationally linked, by a 2A linker peptide, with mCherry. Embryos with isolated muscle fibers that expressed the mCherry reporter were selected for analysis. (B) Experimental setup for SPIM imaging. The 2 dpf embryos, mounted in agarose in a capillary tube, were placed inside an embryo medium-filled chamber. Electrical stimulation to the head was used to evoke a single muscle contraction, and fluorescent GCaMP signal was recorded. (C) GCaMP6-slow signals were recorded from individual fast muscle fibers during a contraction. Loss of RyR1a or RyR3 channels did not alter Ca2+ release; however, loss of RyR1b eliminated all Ca2+ release in fast fibers. (D) GCaMP6-slow signals were recorded from individual slow muscle fibers during a contraction. Loss of RyR1b activity reduced Ca2+ release, whereas loss of RyR1a activity resulted in increased release of Ca2+ in slow fibers. Arrows indicate time at which electrical stimulus was delivered. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
|