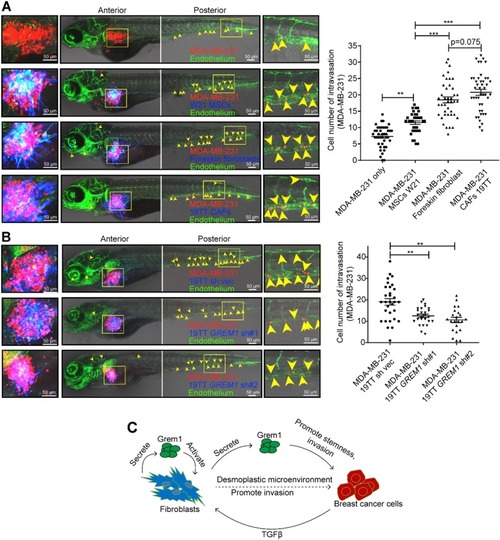
GREM1 knockdown attenuates the ability of 19TT breast cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) to promote breast cancer cell intravasation in a zebrafish co-injection model. a Perivitelline space single injection of MDA-MB-231 cells or co-injection of MDA-MB-231 cells and W21 mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), foreskin fibroblasts, or 19TT CAFs, as indicated. The panel shows the representative images. Green, endothelium of zebrafish; red, mCherry-labeled MDA-MB-231; blue, converted from AmCyan-labeled MSCs or fibroblasts. Yellow arrowheads point to the single intravasated cells in the head and tail regions of zebrafish. Left, cell migration in the perivitelline space; middle, the image of a zebrafish embryo body. Right, visualization of the intravasated cells in the posterior of the embryo. The graph shows the quantification of the number of intravasated cells in each embryonic body at 3 days post-injection (dpi). The results are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m., n = 2. Student’s t test, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. b Perivitelline space co-injection of MDA-MB-231 cells and 19TT CAFs with/without GREM1 knockdown. The panel and graph description are the same as described in a. The results are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m., n = 2. Student’s t test, **P ≤ 0.01. c Schematic of the working model of Grem1 function in breast cancer progression. Grem1 expression in fibroblasts is induced by factors (such as TGFβ from breast cancer cells or maybe other stromal cells (that produce inflammatory cytokines). Grem1 could activate fibroblasts into CAFs. CAFs might present a desmoplastic microenvironment, thereby promote cancer cell invasion. Grem1 itself could promote the stemness and invasion of breast cancer cells
|