Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190730-30
- Publication
- Garland et al., 2019 - Glucocorticoid receptor-dependent induction of cripto-1 (one-eyed pinhead) inhibits zebrafish caudal fin regeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
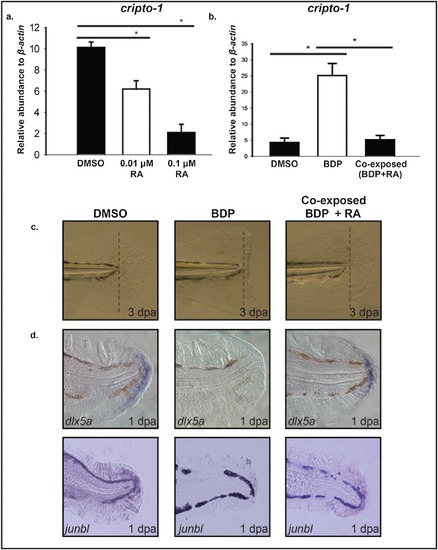
RA exposure suppress cripto-1 expression in the fin tissue and rescues BDP impaired regeneration. a) Caudal fin of 2 days post-fertilization (dpf) embryos were amputated and exposed to DMSO or either 0.01 μM or 0.1 μM retinoic acid (RA). The abundance of cripto-1was estimated in the regenerating fin tissues. The expression of cripto-1 was significantly reduced in a concentration-dependent manner compared to the control. The respective values represent the mean ± SEM and the asterisks indicate statistical significance (One-way ANOVA, n = 3, p < 0.05). b.) 2 dpf larvae were exposed to 0.1 μM RA for 8 h followed by amputation and co-exposure with 0.01 μM RA and DMSO or beclomethasone dipropionate (BDP). The abundance of cripto-1 was evaluated at 1 day post-amputation (dpa) in the regenerating fin tissue by qRT-PCR. Co-exposure with RA significantly suppressed cripto-1 expression compared to BDP exposure. The respective values represent the mean ± SEM and the asterisks indicate statistical significance (One-way ANOVA, n = 3). c). Amputated 2 dpf larvae pre-exposed with 0.1 μM RA were exposed to DMSO, BDP or co exposed with BDP and 0.01 μM RA. Regenerative progression was monitored and pictures were taken at 3 dpa. In each replicated experiment regeneration was restored in approximately 75% embryos co exposed to BDP and RA compared to BDP alone. d) In situ localization of dlx5aand junbl in the regenerating fin tissue at 1 dpa demonstrated restoration of regeneration markers in the caudal fin of larvae co-exposed with BDP and RA. |