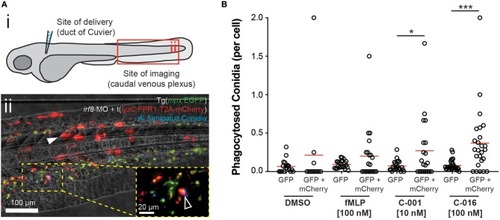
Bifunctional compounds enhance phagocytosis of A. fumigatus conidia by zebrafish neutrophils expressing human FPR1. (A) (i) Diagram of experimental approach: Calcofluor-stained A. fumigatus conidia (blue) are co-delivered with treatments into the circulation via the Duct of Cuvier at 3 days post-fertilization. Imaging is performed at 2 h post-infection at a distal site, the caudal venous plexus, which is rich in leukocytes. (ii) Example image of 3 dpf irf8-MO treated Tg(mpx:EGFP) larva (GFP-labeled neutrophils) with mosaic expression of human FPR1 (traced by mCherry, red fluorescence), 2 h following delivery of calcofluor-labeled (blue fluorescent) A. fumigatus conidia. A GFP/mCherry co-labeled leukocyte containing phagocytosed conidia is indicated in magnified panel (open white arrowhead). Off-target expression of the transgene was also observed in tissues including the somites (full white arrowhead). (B) Treatment with C-001 and C-016 resulted in significantly increased phagocytosis of conidia by GFP/mCherry+ (human FPR1-expressing) neutrophils compared to GFP(only) wild-type cells. Each point represents an infected larva. N ≥ 40 larva scored per condition. Data collated from multiple experiments. Statistics: two-tailed T-test. *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001.
|

