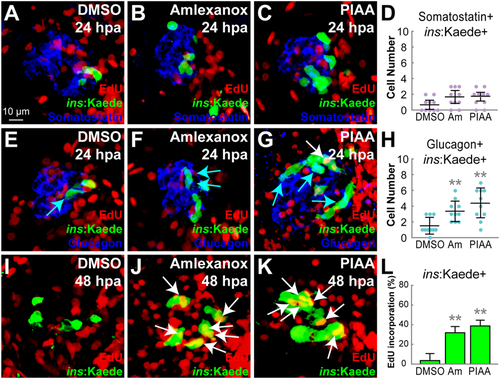
Fig. 4
|
TBK1/IKKε inhibitors have modest effects on α-to-β-cell transdifferentiation but strongly enhance β-cell proliferation. (A–C) Confocal images of [Tg(ins:CFP-NTR)s892; Tg(ins:Kaede)jh6] larvae at 24 hpa, concurrently treated with EdU and DMSO (A), amlexanox (B), or PIAA (C), respectively, from 0–24 hpa, stained for Somatostatin (blue). (D) Quantification of the number (mean ± SD) of Insulin and Somatostatin-double positive cells at 24 hpa (in A-C; 0.7 ± 0.6 (DMSO), 1.7 ± 0.8 (amlexanox), and 1.8 ± 0.5 (PIAA)). (E–G) Confocal images of [Tg(ins:CFP-NTR)s892; Tg(ins:Kaede)jh6] larvae at 24 hpa, concurrently treated with EdU and DMSO (E), amlexanox (F), or PIAA (G), respectively, from 0–24 hpa, stained for Glucagon (blue). Note that the number of Insulin and Glucagon-double positive cells (blue arrows) was increased in TBK1/IKKε-I-treated recovering larvae (F, G) compared to DMSO-treated larvae (E). PIAA-treated larvae also showed an EdU-incorporated β-cell (white arrow) (G). (H) Quantification of the number (mean ± SD) of Insulin and Glucagon-double positive cells at 24 hpa (in E-G; 1.5 ± 1.1 (DMSO), 3.4 ± 1.3 (amlexanox), and 4.4 ± 1.9 (PIAA)). (I–K) Confocal images of [Tg(ins:CFP-NTR)s892; Tg(ins:Kaede)jh6] larvae at 48 hpa, concurrently treated with EdU and DMSO (I), amlexanox (J), or PIAA (K), respectively, from 24–48 hpa. The number of β-cells that incorporated EdU (white arrows) was significantly increased in TBK1/IKKε-I-treated recovering larvae (J, K) compared to DMSO-treated larvae (I). (L) The percentage (mean ± SD) of regenerated β-cells that incorporated EdU at 48 hpa (in I-K; 4.0 ± 7.0% (DMSO), 32.0 ± 6.0% (amlexanox), and 39.0 ± 6.0% (PIAA)). Cells in 20 planes of confocal images from 10 individual larvae were counted per condition. **P < 0.01. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Conditions: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Protruding-mouth to Day 4 |