Fig. 6
|
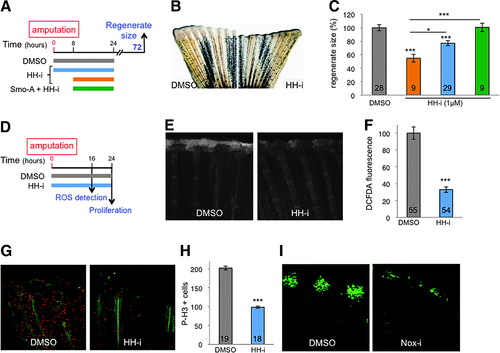
Early HH signaling is necessary for ROS production. (A–C) HH-i added to the water bath from 0 to 24 hpa (blue) or from 8 to 24 hpa (orange) inhibits regeneration, which can be rescued by Smo-A (green). (D–H) Hedgehog inhibition with HH-i (cyclopamine) (D) reduced ROS levels at the amputation plane at 16 hpa (E, F) and stump proliferation at 24 hpa (G, H). (G, H) Immunofluorescence staining for the axonal marker, acetylated tubulin (green), and for the mitotic cell marker, phosphorylated histone H3 (red). (I) Nox-i added to the water bath from 0 to 24 hpa reduced the number of Shh-positive cells detected at 48 hpa. Shh-positive cells were visualized by immunodetection of the GFP in shh:GFP transgenic fish. Error bars represent the SEM (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001). n Values are indicated at the bottom of each column of the graphs. HH-i, hedgehog inhibitor, cyclopamine; Smo-A, smoothened agonist. |