Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160926-36
- Publication
- Bhuiyan et al., 2016 - Acinetobacter baumannii phenylacetic acid metabolism influences infection outcome through a direct effect on neutrophil chemotaxis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
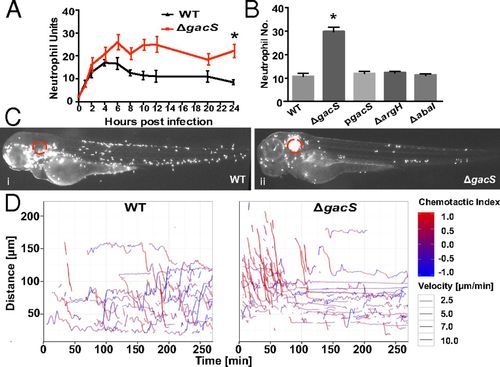
Altered in vivo neutrophil migratory patterns during A. baumannii infection. (A) Localized somatic muscle infection with A. baumannii ΔgacS led to greater neutrophil units at the site of infection and a loss of migration away compared with wild-type A. baumannii infection (mean ± SEM from three biological replicates). (B) Neutrophil units at the site of a localized somatic muscle infection 48 hpi showed restoration of neutrophil numbers with gacS complementation (pgacS) and no abnormalities with other A. baumannii virulence-associated mutants (ΔargH, ΔabaI; mean ± SEM, three biological replicates). (C) Infection of the otic vesicle (red circle) with wild-type A. baumannii (i) and ΔgacS (ii) imaged at 48 hpi. (Magnification: 10×.) (D) Cell tracking analysis of neutrophil movement after infection with WT and ΔgacS strains. A chemotactic index (red, movement toward infection; blue, movement away) and velocity (thickness of the line) are indicated (representative experiment from five biological replicates). Asterisks in A and B denote comparison between wild-type A. baumannii and ΔgacS (*P ≤ 0.05). |