Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160819-23
- Publication
- Halloum et al., 2016 - Deletion of a dehydratase important for intracellular growth and cording renders rough Mycobacterium abscessus avirulent
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
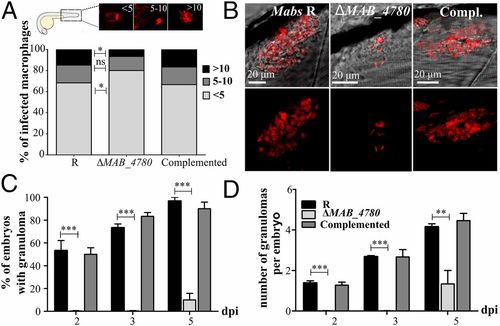
The intracellular growth defect of ΔMAB_4780 is associated with impaired granuloma formation in zebrafish. (A) Average proportion of infected macrophages classified as mildly, moderately, or highly infected (containing <5, 5-10, and >10 bacteria, respectively) at 24 hpi. Significance was assessed by a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple posttest (*P < 0.05). Top enclosed panel shows representative infected macrophage of each class. (B) Maximum intensity projection of confocal images showing representative granuloma-like structures in 3 dpi larvae i.v.-infected with Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, or the complemented strain expressing tdTomato. (C) Kinetics of granuloma formation in intravenously-infected embryos (~150 cfu; n = 30). Histograms represent means calculated from three independent experiments. Overall, ΔMAB_4780 mutant-infected embryos developed significantly less granuloma compared with the R and complemented strains. (n = 30; Fisher’s exact test; ***P < 0.001). Error bars represent the SEM. (D) Number of granulomas per embryo harboring granuloma. A significant reduction in the number of granulomas per embryo is found in embryos infected with ΔMAB_4780 compared with R-infected embryos. The statistical test used was the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple posttest (n = 30); **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Error bars represent the SEM. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Protruding-mouth to Day 6 |