Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160811-13
- Publication
- Bolar et al., 2016 - Heterozygous Loss-of-Function SEC61A1 Mutations Cause Autosomal-Dominant Tubulo-Interstitial and Glomerulocystic Kidney Disease with Anemia
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
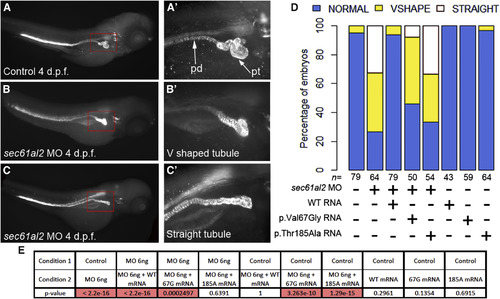
Suppression of SEC61A1 Leads to Pronephric Tubular Atrophy in Zebrafish (A-C) Whole-mount immunostaining of 4 days post-fertilization (dpf) zebrafish larvae with anti-Na+/K+-ATPase alpha subunit monoclonal antibody (±6F) shows the overall anatomy of the pronephric ducts (pd) and pronephric tubules (pt), which become progressively convoluted in control larvae. Three levels of convolution were assessed: convoluted (normal) (A and A′), V-shaped (B and B′), and straight pronephric tubule (C and C′). The pronephric ducts are normal. (D) Qualitative scoring of the tubular atrophy was performed in larvae batches injected with sec61al2 MO alone; MO and mutant (p.Thr185Ala) RNA or (p.Val67Gly) RNA; MO and wild-type (WT) capped-RNA; WT and mutant RNAs alone; and control. (E) Results of Fisher’s exact test conducted between pairs of conditions. The significant p values (< 0.05) are highlighted in red. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |