Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160726-19
- Publication
- Umeda et al., 2016 - Position- and quantity-dependent responses in zebrafish turning behavior
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
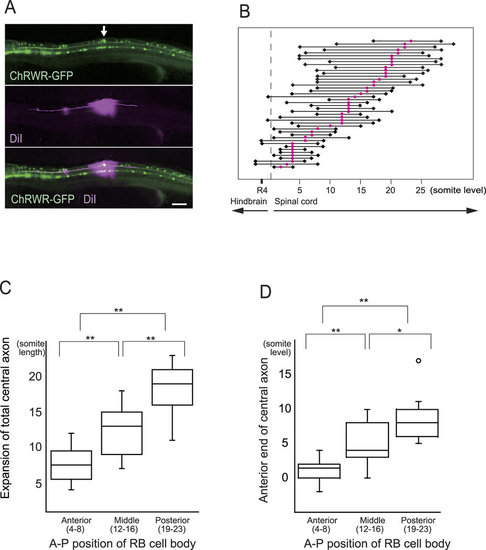
Extent of RB central axons along different A-P cellular position. (A) (Upper panel) Ionophoretic diI injection was guided with GFP expressed by RB neurons (arrow). Scale bar 100 µm. (Middle) Ascending and descending axons were fluorescently labeled by anterograde fluid expansion. (Lower) Merged image of GFP and diI fluorescence. (B) Extent of RB central axon extension from each individual neuron. Red circles denote cell bodies, and black rhombuses indicate ends of ascending and descending axons. Only small numbers of axons reached the hindbrain level, with the axon endings showing variation even among neurons at the same A-P level, whereas anterior neurons tended to extend more anteriorly. (C) Sum length of ascending and descending axons in three A-P groups of RB neurons. Posterior neurons extend longer axons within the spinal cord. Box plots show, 25, 50, and 75th percentiles (boxes) and 2.5 and 97.5th (whiskers). Mean values were 7.5, 13.0, and 19.0 for anterior (n = 12), middle (n = 13), and posterior neurons (n = 13), respectively. **P < 0.01 by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. (D) Comparison of anterior ends of central axons. Topographic A-P arrangement was statistically maintained within the spinal cord. Mean values were 1.5, 4.0, and 8.0 from the anterior, and numbers of neurons were as in C. *and **denote P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Open circle indicates outlier. |