Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150408-2
- Publication
- Sawada et al., 2015 - In vivo loss of function study reveals the short stature homeobox-containing (shox) gene plays indispensable roles in early embryonic growth and bone formation in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
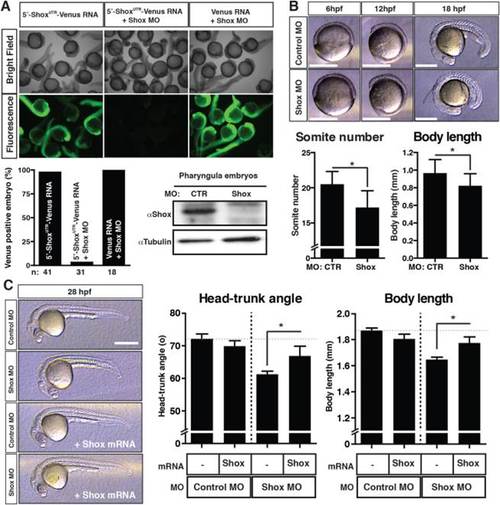
The effects of loss of Shox expression in developing embryo at the early pharyngula stage. A: Shox MO specificity in zebrafish embryo. The translation block Shox MO (8 ng/embryo) and in vitro synthesized capped Venus mRNA (250 pg/embryo) were co-injected at 1–2-cell-stage embryos, and the Venus signal was checked at 27hpf embryos. n: number of embryos assessed in the analysis. Immunoblot analysis of endogenous Shox and tubulin proteins are shown. B: The phenotypes of Shox MO-injected morphant embryos at gastrula-segmentation stages. Bars = 0.5 mm. The somite numbers and body length at 18hpf embryos are shown. Values are represented as mean±S.D. (n=18–20). Asterisk (*) represents statistical significance (P<0.05). C: Embryonic growth at the pharyngula stages. Either control MO or Shox MO (8 ng/embryo), or a combination of MO and the MO-resistant Flag-Shox mRNA (500 pg/embryo) was injected into 1–2-cell-stage embryos. The embryos were raised to 28hpf and the head-trunk angle and body length were measured. Representative embryos are displayed in the left panels. Bars = 0.5 mm. Values are represented as mean±S.D. (n=13–28). Asterisk (*) represents statistical significance (P<0.05). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | 14-19 somites to Prim-5 |