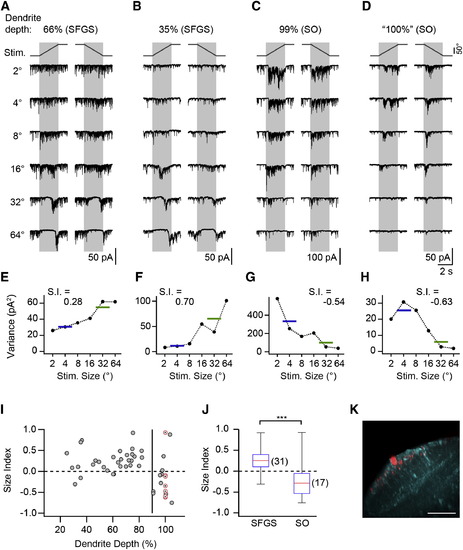
SINs Receive Size-Selective Excitatory Input (A) Synaptic current in a SIN with dendrite in upper SFGS. Note the strong background current, which is suppressed during the presentation of larger targets, and subsequent rebound from input suppression. (B) Recording from SIN with dendrites in deep SFGS with size-tuned synaptic input. (C) Recording from SIN with dendrites in the superficial SO. Note the increase in synaptic current during small target presentation. (D) Recording from a SIN in the Oh:GCaMP6s line with dendrites in superficial SO, preselected because of small-size-driven Ca2+ signals. (E–H) Current variance of cells shown in (A)–(D) as a function of target size. Horizontal lines indicate the mean variance for small and large targets, respectively. (I) Size index of SINs versus dendritic depth. Gray symbols indicate SINs randomly sampled in the pou4f3:GFP line (n = 41). Red, crossed circles indicate SINs preselected in the Oh:GCaMP6s line (nominal dendrite depth 100%, n = 7). The vertical line indicates 90% dendrite depth. (J) Size index of SINs with dendrites arborizing within 20%–90% of retinorecipient neuropil (SFGS) and e90% (SO) were significantly different (p = 3.5 × 104, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). The red line indicates the median, the box indicates the 25%–75%-quartile range, and error bars indicate the full range of data. (K) Example of small-size-selective SIN in the Oh:GCaMP6s line. The same cell as in (D) is shown. The maximum-intensity projection is oriented as in Figure 3C. GCaMP6s expression shown in cyan. Scale bar, 40 µm. See also Figure S3.
|

