Fig. S4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-141231-1
- Publication
- Schulte et al., 2014 - Targeted resequencing and systematic in vivo functional testing identifies rare variants in MEIS1 as significant contributors to restless legs syndrome
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
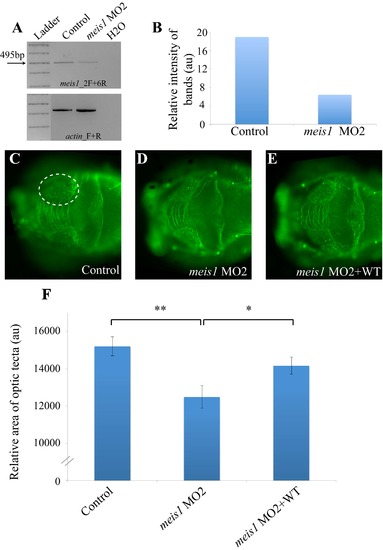
In vivo complementation of MEIS1, using a previously reported MO (meis1_MO2) against the acceptor splice junction of exon 2. (A) The effect of meis1_MO1 targeting the donor site of exon 2 and inducing skipping of exons 2-7 has been evaluated previously5. (B) We here amplified the cDNA sequence between exons 2-6 in control embryos and morphants injected with 9ng meis1_MO2 and detect only ~30% of the wild-type RNA message in the morphant embryos. (C-F) Suppression of meis1 results in a reduction of the size of the optic tectum by 20-30%, similar to the phenotype observed when using meis1_MO1 that can be significantly and reproducibly rescued upon co-injection with wt human MEIS1 mRNA. Asterisks denote significance levels as determined by Student`s t-test (** p-value < 0.005; * p-value < 0.05). MO=morpholino, wt=wildtype |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |