Fig. S6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140522-62
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2014 - An evolutionarily conserved long noncoding RNA TUNA controls pluripotency and neural lineage commitment
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
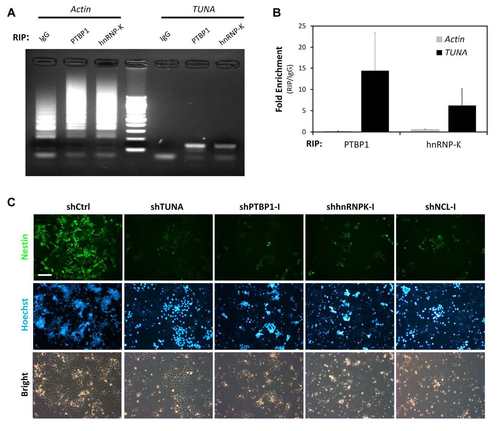
Functional analysis of TUNA-associated RBPs. (A) Verification of RNA-protein interaction by RIP. CCE mESCs were crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde and incubated with anti-hnRNP-K or anti-PTBP1. IgG was used as a negative control. After pulldown, RNA was extracted and RT-PCR analysis of TUNA or Actb was performed on equal concentrations of RNA. PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The correct size of the PCR amplicons is ~150 bp. (B) Enrichment of TUNA or Actb in RIPs performed with anti-PTBP1 or anti-hnRNP-K compared with control IgG immunoprecipitates. Data are the mean ± SD of triplicates. (C) In vitro neural differentiation is impaired by depletion of TUNA-associated RBPs. CCE mESCs were differentiated in monolayer cultures for two days and then transduced with shRNAs targeting TUNA, PTBP1, hnRNP-K, or NCL. Cells were analyzed at five days post-transduction. Top and middle rows show fluorescence micrographs of Nestin and Hoechst nuclear staining, respectively. Bottom row shows the bright-field images. Scale bars, 200 µm. |