Fig. S2
|
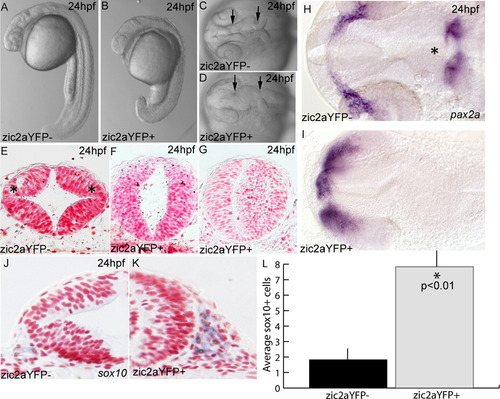
Expression of a zic2aYFP fusion protein causes developmental defects. (A–D) Embryos induced by heat shock to express the zic2aYFP fusion protein at 10 hpf have a shortened anterior–posterior axis and a characteristic kinked neural tube with a closed midbrain ventricle (located between arrows in C,D; 75/87, 4 exp.). (E) Zic2aYFP-negative siblings have distinct dorsolateral hinge points in the midbrain (asterisks in E; 2/2, 2 exp.). (F,G) Zic2aYFP induction at 10 hpf does not always preclude lumen formation, but does eliminate dorsolateral hinge points (4/4, 2 exp.). (H,I) Expression of pax2a reveals patterning defects in the retina, optic stalks and mid-hindbrain boundary of Zic2aYFP-expressing embryos (asterisk in H, 8/10, 1 exp). (J,K) Zic2aYFP-expressing embryos have more sox10-positive cells lateral to the midbrain. (L) Comparison of average numbers of sox10-positive cells in half of the neural tube in a single section (averaged from 3 randomly selected midbrain-level sections per embryo, 2 embryos per condition, 1 exp). Error bars are standard error and significance was tested with a Student′s t-test. A,B are lateral views, anterior to the left. C,D,H,I are dorsal views, anterior to the left. E–G, J, K are transverse sections through the midbrain. Green dots were added to mark cells counted as sox10-positive. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 380(1), Teslaa, J.J., Keller, A.N., Nyholm, M.K., and Grinblat, Y., Zebrafish Zic2a and Zic2b regulate neural crest and craniofacial development, 73-86, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.