|
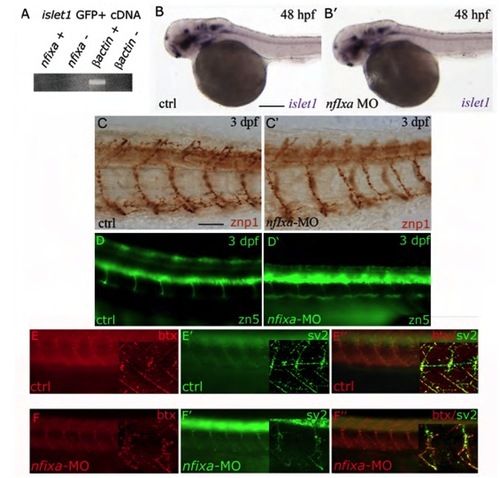
Nfixa loss of function does not influence motoneurons development (A) RT-PCR performed on cDNA of motoneurons sorted from islet1 GFP transgenic embryos at 48 hpf. nfixa is not expressed in this cell population. (B,B′) islet1 expression pattern in nfixa-MO embryos at 48 hpf does not present differences in comparison with control embryos, suggesting that motoneurons are correctly formed. (C-D′) Axonal projections of primary (C,C′) and secondary motoneurons (D,D′) visualized by znp1 and zn-5 antibodies, respectively, are correctly formed in nfixa-MO-injected embryos. (E-F′′) Synapses were labeled with bungarotoxin (BTX red, postsynaptic AChRs) and SV2 (green, presynaptic vesicles) antibodies. The co-localization of both signals in control (E′′) and nfixa-MO injected (F′) embryos showed functional neuromuscular synapses. Main panels are images taken on a fluorescence microscope; insets show single-plane confocal images/projections from a confocal z-stack.
|