Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130318-11
- Publication
- Lu et al., 2013 - Failure in closure of the anterior neural tube causes left isomerization of the zebrafish epithalamus
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
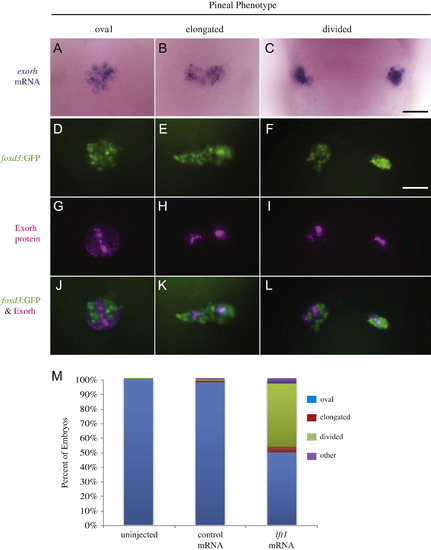
Projection neuron and photoreceptor differentiation occurs in the pineal glands of Lft1 overexpressing embryos with open neural tubes. ((A)–(C)) The photoreceptor specific gene exorh is expressed in embryos with all three pineal phenotypes (n=21 oval, n=2 elongated, n=6 divided). ((D)–(L)) Embryos were analyzed for both foxd3:GFP transgene expression and Exorh protein expression, and representative embryos with an oval pineal ((D), (G) and (J)), with an elongated pineal ((E), (H) and (K)), and a divided pineal ((F), (I) and (L)) are shown. ((D)–(F)) are images of the foxd3:GFP expression, ((G)–(I)) are images of the Exorh immunostaining, and ((J)–(L)) are overlays of the two expression patterns. Note that in ((J)–(L)), foxd3:GFP and Exorh are expressed in distinct regions of the pineal, suggesting the foxd3:GFP transgene is primarily found in pineal projection neurons at this stage of development (n=36 oval, n=4 elongated, n=11 divided). (M) Percentage of lft1 mRNA injected embryos expressing the foxd3:GFP transgene in an oval pattern (closed anterior neural tube), or elongated or divided pattern (open neural tube). n>120 embryos. All embryos were at 48 hpf. All images are dorsal views, anterior to the top. Scale bars=25 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 374(2), Lu, P.N., Lund, C., Khuansuwan, S., Schumann, A., Harney-Tolo, M., Gamse, J.T., and Liang, J.O., Failure in closure of the anterior neural tube causes left isomerization of the zebrafish epithalamus, 333-344, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.