FIGURE
Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120611-7
- Publication
- Chen et al., 2012 - Heterogeneity across the dorso-ventral axis in zebrafish EVL is regulated by a novel module consisting of sox, snail1a and max genes
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. S2
|
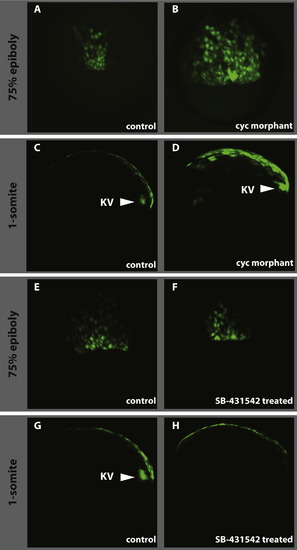
Effect of loss of Nodal signalling on dEVL and Kupffer’s vesicle formation. As compared to control (A and E), the cyc morpholino injections result in the expansion of the dorsal GFP domain (B) whereas the drug treatment doesn’t have any effect on dEVL (F). As in wild type (C) and control treated (G), Kupffer’s vesicle forms in cyc morphant (D, KV and arrowhead) where the vesicle is absent in SB-431542 treated embryos (H). A, B, E and F dorsal view at 60–70% epiboly. C, D, G, and H lateral view at 1-somite stage anterior is to the left. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 129(1-4), Chen, Y.Y., Harris, M.P., Levesque, M.P., Nüsslein-Volhard, C., and Sonawane, M., Heterogeneity across the dorso-ventral axis in zebrafish EVL is regulated by a novel module consisting of sox, snail1a and max genes, 13-23, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.