Fig. S2
|
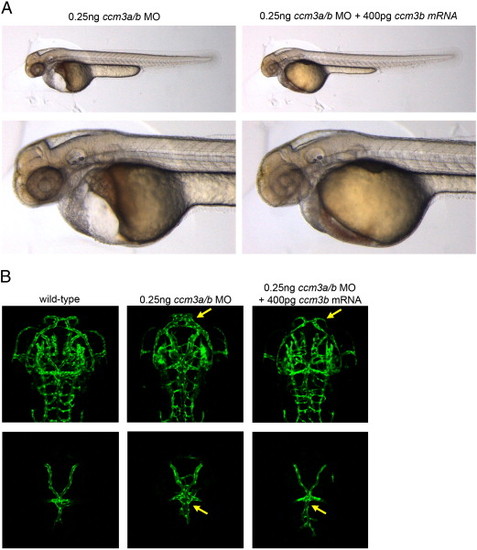
Cardiovascular defects caused by morpholino-knockdown of ccm3a/b can be rescued by overexpression of ccm3b mRNA. (A) Light images of ccm3b mRNA injected and non-injected ccm3a/b morphant embryos at 54 hpf. The pronounced pericardial edema and circulatory block observed in 93% of the embryos upon 0.25 ng ccm3a/b morpholino injection (n = 83) are rescued by co-injection of 400 pg ccm3b mRNA. 63% of ccm3a/b morphant embryos injected with ccm3b mRNA had normal heart morphology and completely restored circulation (n = 76). (B) Confocal z-stack projections of dorsal head vasculature in ccm3a/b morphants indicate a decrease in the dilation and misconnections in cranial vessels upon ccm3b mRNA injection (yellow arrows). |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 362(2), Yoruk, B., Gillers, B.S., Chi, N.C., and Scott, I.C., Ccm3 functions in a manner distinct from Ccm1 and Ccm2 in a zebrafish model of CCM vascular disease, 121-131, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.