Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110622-120
- Publication
- Lupo et al., 2011 - Retinoic acid receptor signaling regulates choroid fissure closure through independent mechanisms in the ventral optic cup and periocular mesenchyme
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
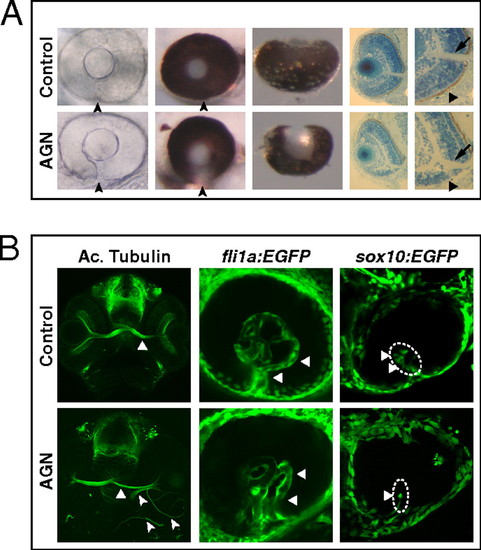
Inhibition of RAR signaling causes coloboma in zebrafish. (A) Coloboma (arrowheads) in embryos treated with 2.5–5 μM AGN from 3 to 6 s. (Left) Lateral view of 48-hpf phenylthiourea-treated embryos. (Center) Lateral (Center Left) and ventral (Center Right) views of 60-hpf eyes. (Right) Sections of 60-hpf eyes showing the lack of retinal pigmented epithelium (triangles) and a shortening of the retina ventral to the optic nerve head (arrows) in the AGN-treated embryo. (B, Left) Immunostaining with an anti-acetylated (Ac.) tubulin antibody at 48–50 hpf, showing abnormal retinal axon trajectories in the AGN-treated embryo (arrowheads), besides the normal contralateral projection (triangles). (Center) fli1a:EGFP transgenic embryos at 48 hpf. The AGN-treated embryo exhibits disrupted vascularization (triangles). (Right) sox10:EGFP transgenic embryos at 32–36 hpf. The AGN-treated embryo shows less POM cells within the choroid fissure (triangles). |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-15 to Long-pec |