Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100616-16
- Publication
- Stewart et al., 2010 - Phosphatase-Dependent and -Independent Functions of Shp2 in Neural Crest Cells Underlie LEOPARD Syndrome Pathogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
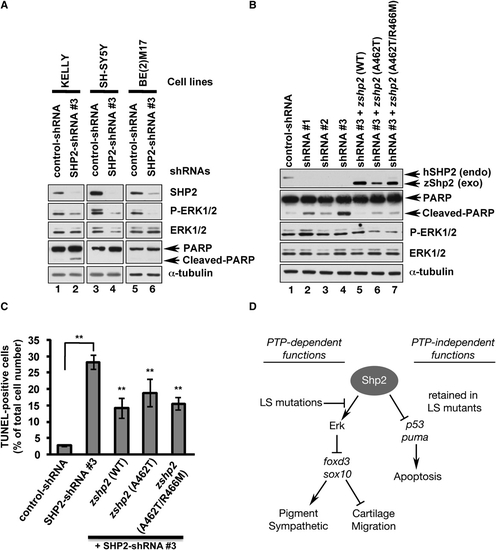
PTP- and ERK-Independent Function Of SHP2 Is Conserved in Neuroblastoma Cells (A) Immunoblot of lysates from neuroblastoma cell lines transduced with control shRNA or SHP2-shRNA#3. SHP2 and p-ERK1/2 levels are reduced by shRNA#3 in all cell lines (lanes 2, 4, 6), but only KELLY cells exhibit increased PARP cleavage (lane 2). (B) KELLY cells transduced with SHP2-shRNAs (lanes 1–3) have decreased SHP2 and ERK1/2 levels and increased PARP cleavage (compare lane 1 to lanes 2–4). PARP cleavage caused by shRNA#3 is rescued by cotransduction of wild-type zebrafish zshp2, PTP-impaired (A462T) or PTP-dead (A462T/R466M) zshp2. Exogenous WT zshp2 partially rescues p-ERK1/2 levels (while LS or LS/PTP-dead zshp2 have mild dominant-negative effects). (C) shRNA#3 induces cell death in ∼30% of the infected KELLY cells (TUNEL stain). Cotransduction with zebrafish constructs reduces the cell death caused by shRNA#3. **p < 0.001. (D) Model showing phosphatase-dependent and -independent functions of Shp2 during neural crest development. See text for details and Figure S4 for supporting data. Error bars correspond to standard deviation of the mean. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 18(5), Stewart, R.A., Sanda, T., Widlund, H.R., Zhu, S., Swanson, K.D., Hurley, A.D., Bentires-Alj, M., Fisher, D.E., Kontaridis, M.I., Look, A.T., and Neel, B.G., Phosphatase-Dependent and -Independent Functions of Shp2 in Neural Crest Cells Underlie LEOPARD Syndrome Pathogenesis, 750-762, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell