Fig. 2
|
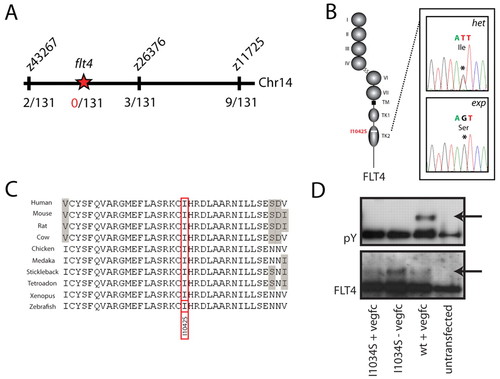
A mutation in the flt4 kinase domain is responsible for the expando phenotype. (A) Meiotic mapping links the expando locus to a region of chromosome 14 containing flt4. Analysis of 131 zebrafish embryos (262 meioses) identifies two recombination events at the marker z43267 and three independent recombinants at the marker z26376, thereby localising the mutation to a region containing flt4. (B,C) Sequencing of the coding exons of flt4 reveals a T>G mutation (see chromatogram in B) that changes a highly conserved isoleucine to a serine at position 1042 of the predicted zebrafish Flt4 protein sequence. Flt4 receptor structure is depicted, with Ig domain (I-VII), transmembrane domain (TM) and split tyrosine kinase domain (TK1 and TK2). Alignment of conserved sequences (C) demonstrates that I1042 is a conserved residue, with grey shading indicating non-conserved residues. (D) Tyrosine phosphorylation (pY; upper panel, phosphotyrosine blot) was seen upon in vitro stimulation with VEGFC of wild-type human FLT4, but not of I1034S mutant FLT4. Lower panel (Flt4 protein blot) indicates the presence of FLT4 protein post-transfection in the assayed samples. |