Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090506-32
- Publication
- Waxman et al., 2009 - Increased Hox activity mimics the teratogenic effects of excess retinoic acid signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
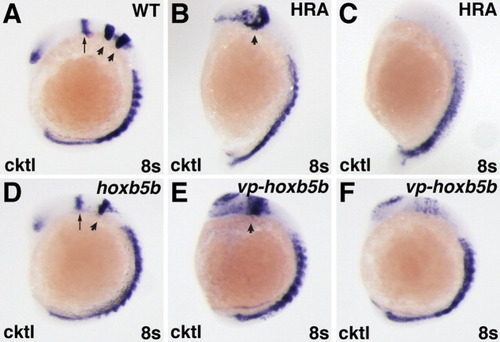
Increased RA signaling and Hox activity have similar effects on the anterior CNS. A-F: In situ hybridizations at the 8-somite stage with a cocktail (cktl) of probes including pax2a (eye and MHB), krox-20/egr2b (rhombomeres 3 and 5), and myod (somites). B,C,E,F: High RA treatment (HRA) or injection with 60 pg of vp-hoxb5b mRNA cause severe posteriorization phenotypes that vary between individual embryos. B,E: High RA treatment and 60 pg vp-hoxb5b mRNA injection can truncate the anterior CNS, eliminate the MHB, and dramatically expand the posterior hindbrain. C,F: High RA treatment and 60 pg vp-hoxb5b mRNA injection can also dramatically reduce or eliminate anterior CNS markers. D: 150 pg hoxb5b mRNA injection causes loss of rhombomere 3, consistent with what has been shown previously for hoxb5b mRNA injection and for modest increases in RA signaling (Bruce et al.,[2001]; Hernandez et al.,[2007]). All images are lateral views, with dorsal to the right and anterior up. Arrows in A and D, MHB; arrowheads in A, rhombomeres 3 and 5; arrowheads in B, D, E, rhombomere 5. |