Fig. 4
|
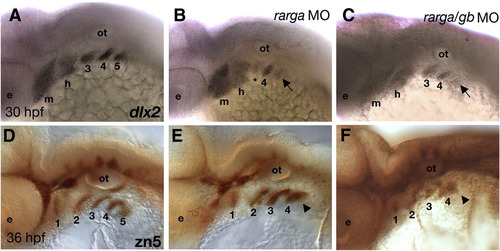
Depletion of rarga alone disrupts posterior pharyngeal arches. Lateral views, anterior to the left. (A, D) Controls. (B, E) rarga morphants (C, F) rarga/rargb double morphants. (A–C) Whole mount in situ hybridization to detect dlx2 mRNA reveals reductions in migrating neural crest cells in arches 3–5 (arrows) in both single (B; 28/30) and double (C; 35/35) morphants. (D–F) Whole mount, immunostaining with the zn-5 antibody reveals reductions in the pharyngeal pouch endoderm (particularly pouch #5, arrowheads) in these arches, but no defects in zn5+ cells in the hindbrain or cranial ganglia in single (E) and double (F) morphants. Abbreviations: e, eye; m, mandibular; h, hyoid; ot, otic vesicle. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-15 to Prim-25 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-25 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 325(1), Linville, A., Radtke, K., Waxman, J.S., Yelon, D., and Schilling, T.F., Combinatorial roles for zebrafish retinoic acid receptors in the hindbrain, limbs and pharyngeal arches, 60-70, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.