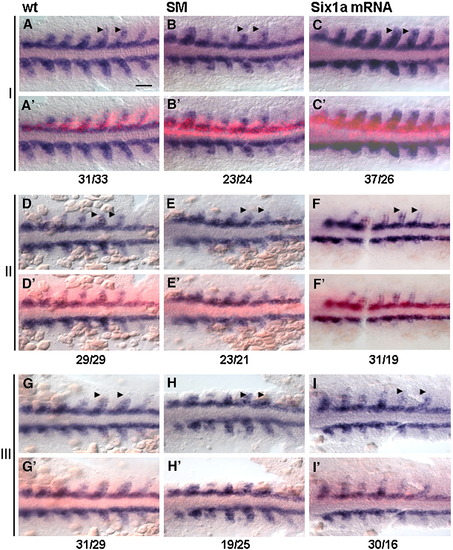
six1a mRNA rescues myog expression in fast muscle precursor region of SM morphants. Flat mounts of embryos after WISH for myog at 9 s. Three sets of embryos from three independent experiments are shown (I–III; n = 3 for each control, morphant and rescue). The bright-field (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and I) and composite bright-field/fluorescent images to visualize Texas Red on injected side (A′, B′, C′, D′, E′, F′, G′, H′, and I′). The uninjected side (lack of red fluorescence) served as an internal control. Opposing pairs of somites were compared. One-sided injection of Texas Red-dextran does not affect myog expression in wild-type (wt, left column). Expression of myog is reduced in the fast muscle precursors in SM morphants with one-sided injection of Texas Red-dextran (SM, middle column). six1a mRNA rescues myog expression in the fast muscle precursor region on the injected side of SM morphants (Six1a mRNA, right column). Arrowheads mark myog expression in fast muscle precursors. Scale bar, 100 μm. Numbers of myog expressing fast cells on the injected side versus the number of cells on the control side of the embryo are shown as a ratio below.
|

