Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080529-38
- Publication
- Preger et al., 2004 - Alternative splicing generates an isoform of the human Sef gene with altered subcellular localization and specificity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
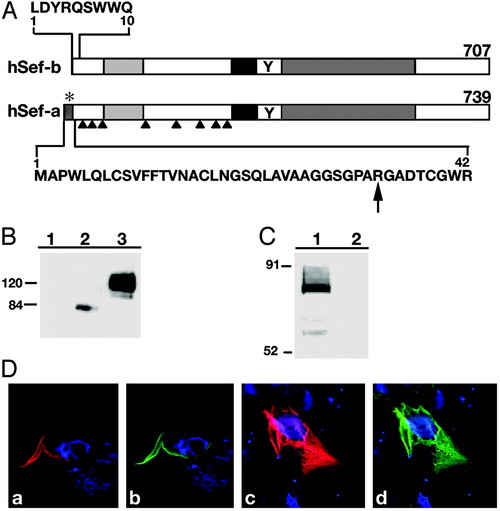
Schematic representation of hSef-a and hSef-b-(A) Residues unique to each Sef isoform are shown in bold letters. *, signal for secretion; arrows, potential N-linked glycosylation sites; black box, transmembrane domain; Y, putative tyrosine phosphorylation site; light and dark gray boxes, Ig-like domain and the IL-17R-like domain. (B) Identification of hSef products. HEK 293 cells were transiently transfected with control empty vector (lane 1) or Myc-tagged hSef-b or hSef-a vectors (lanes 2 and 3, respectively). Equal amounts of protein were subjected to gel electrophoresis, and hSef products were identified by immunoblotting with α-myc antibody. (C) In vitro translation of hSef-b. Lane 1, translation in the presence of hSef-b vector; lane 2, translation in the presence of an empty vector. The assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Products were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and visualized by phosphoimaging. (D) Subcellular localization of hSef isoforms. HEK 293 cells, transfected with myc-tagged hSef-a (a and b) or myc-tagged hSef-b (c and d) expression vectors, were fixed 48 h later and stained with α-myc (red; a and c) or α-hSef antibody (green; b and d). Nuclei were counterstained with bisbenzimide (blue). |