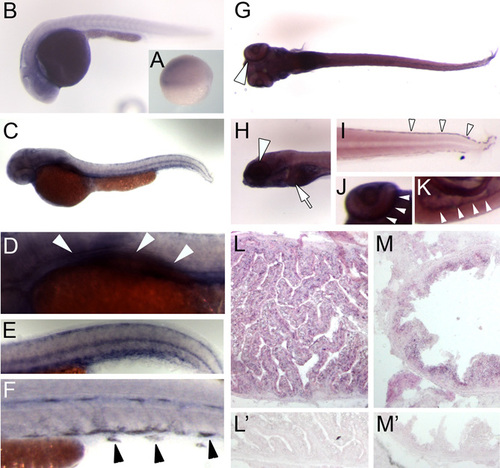
vam6 mRNA is widely expressed during zebrafish development. Whole-mount in situ hybridisation detecting vam6 mRNA expression at different stages of development (A-K) and in adult tissues (L,M) of wild-type zebrafish. (A) Shield stage embryo (6 hpf); vam6 mRNA expression is comparatively weak in all cells of this stage. (B) 24 hpf embryo; at this stage vam6 is widely expressed with the highest levels in the developing brain. (C-F) 48 hpf embryo; vam6 expression has increased compared with earlier stages. Expression is highest in the head region, the region of the developing liver and intestinal tract (D; arrowheads) and in the skin melanocytes (E,F; arrowheads). (G-K) 5 dpf larva; ventral views (G,J) and lateral views (H,I,K). As in earlier stages, vam6 mRNA is widely expressed, but at higher levels than before. Strong expression can be detected in the peripheral retina (region of the RPE; arrowheads in G, H and J), the liver (H; arrow), the melanocytes of the skin (I; arrowheads) and the intestinal tract (K; arrowheads). (L,L′) Expression of vam6 mRNA in the adult zebrafish liver. Panel L′ shows the corresponding sense probe. (M,M′) vam6 mRNA expression in the cells lining the intestinal tract in the adult zebrafish. M′ shows the corresponding sense probe.
|

