Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070822-42
- Publication
- Kim et al., 2007 - Lrrc10 is required for early heart development and function in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
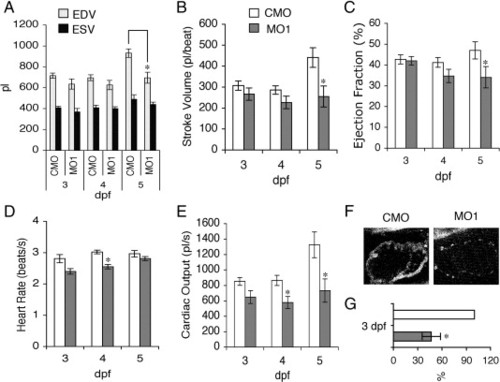
Reduction of zLrrc10 expression causes the defects in heart function. (A) Zebrafish embryos were injected with MO1 or CMO as indicated. To determine EDV and ESV, time-lapse recording was used to follow ventricular movement from a lateral view in embryos at 3–5 dpf. (B) Stroke volume was calculated by subtracting ESV from EDV. (C) Ejection fraction (%) = (EDV - ESV) / EDV × 100. (D) Heart rate was calculated from the number of frames captured during three consecutive, complete ventricular contractions in the time-lapse recordings. (E) Cardiac output was calculated as the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Values are mean ± standard error of the mean with n = 10. An asterisk indicates a significant difference in values between the morphants and control at p < 0.05. (F) Representative fluorescence intensity images of the embryonic hearts are shown in vivo in lateral views with the head to the right using multiphoton microscopy. All images of the control and morphant embryos were obtained at 3 dpf under identical experimental conditions at 780 nm excitation. (G) Relative amounts of NADH were calculated when the control value was set at 100%. n = 4. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Protruding-mouth to Day 5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 308(2), Kim, K.H., Antkiewicz, D.S., Yan, L., Eliceir, K.W., Heideman, W., Peterson, R.E., and Lee, Y., Lrrc10 is required for early heart development and function in zebrafish, 494-506, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.