- Title
-
Lrrc10 is required for early heart development and function in zebrafish
- Authors
- Kim, K.H., Antkiewicz, D.S., Yan, L., Eliceir, K.W., Heideman, W., Peterson, R.E., and Lee, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
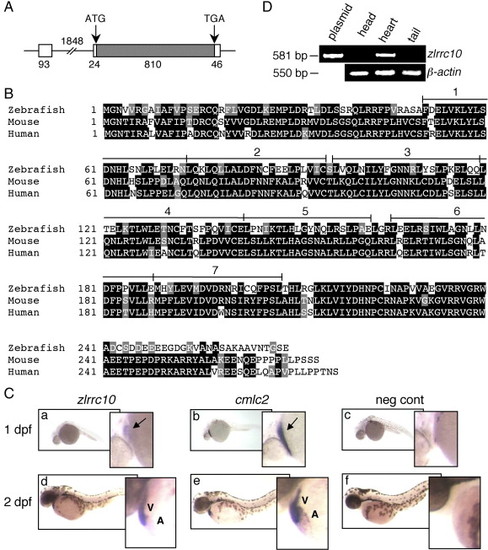
Cardiac-specific expression of zlrrc10. (A) The genomic structure of zlrrc10. The full-length zlrrc10 cDNA consists of two exons. The size of exons, intron and the 5′ and 3′ UTR regions are shown in bp. The amino acid coding regions are represented by the hatched box. (B) An alignment of zebrafish, mouse and human LRRC10 amino acid sequences. Identical residues between all three species are shaded black, and the residues with similar characteristics are shaded gray. The conserved seven LRR motifs are numbered. (C) Cardiac-specific expression of lrrc10 in zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos at 1 dpf (a–c) and 2 dpf (d–f) were subjected to whole-mount in situ hybridization using digoxigenin labeled zlrrc10 antisense cRNA probes (a, d). cmlc2 antisense cRNA probe (b and e) was used for positive control to visualize the heart. Negative control was hybridized with sense zlrrc10 probe (c and f). Arrows indicate the linear heart region that expresses zlrrc10 and cmlc2. A and V indicate the atrium and ventricle, respectively. (D) Cardiac-specific expression of zlrrc10 in adult zebrafish. RT-PCR analysis was performed using total RNA isolated from three different parts of adult zebrafish as indicated. The zlrrc10 PCR products of 581 bp were visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis. The plasmid pCRII-TOPO-zlrrc10 was used as positive control for the amplification reactions. RT-PCR of β-actin was performed as a loading control. |
|
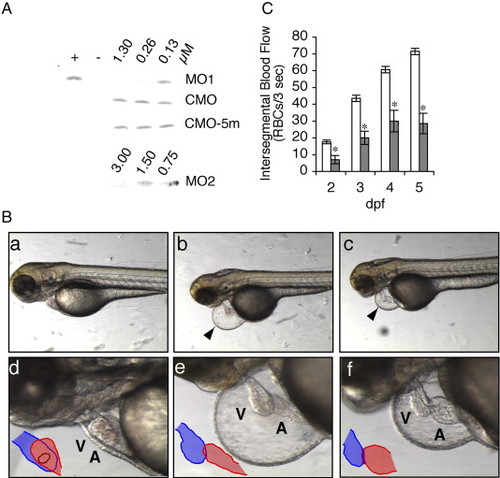
Effects of zlrrc10-MO1 on the zebrafish heart morphology and blood flow. (A) The effect of zlrrc10-MOs on blocking translation of zlrrc10. zlrrc10 cDNA yielded a [35S]-methionine labeled 31 kDa protein by in vitro transcription and translation reaction (+). Negative control (-) was incubated without template plasmid. To determine the effect of zlrrc10-MOs, zlrrc10 cDNA was in vitro translated in the presence of MO1 or MO2. To confirm the specificity of zlrrc10 MOs, two control morpholinos, CMO or CMO-5m were used. The final concentrations of morpholinos in the reaction are indicated. (B) Knockdown of Lrrc10 caused heart defects. CMO (a and d) and MO1 (b, c, e, and f) injected zebrafish were imaged at 3 dpf. d–f are high-power images of a–c, respectively, which show heart looping defects of the morphants (e and f). The arrowhead indicates a large pericardial edema. Blue and red indicate the ventricle and atrium, respectively. A, atrium; V, ventricle. (C) Reduced blood flow in the morphants. Zebrafish embryos were injected with zlrrc10-MO1 (hatched bar) or CMO (open bar). RBC perfusion rates in an intersegmental vessel were determined between 2 and 5 dpf as described in Materials and methods section. An asterisk indicates a significant difference in values between the test CMO and the MO1 at p < 0.05. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
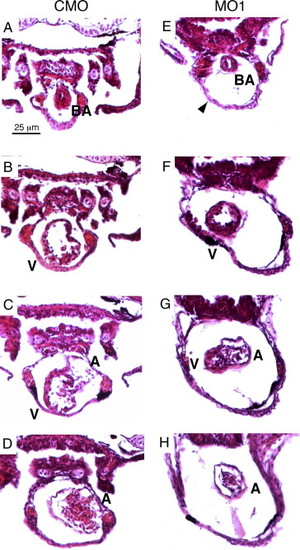
Histological analysis reveals cardiac defects in the zlrrc10 morphants. Zebrafish embryos injected with CMO (A–D) and MO1 (E–H) were fixed at 4 dpf and paraffin embedded. The embryos were sectioned (10 μm) and stained with H&E. Serial transverse sections are shown from the anterior end at the top of the figure and progressing to the posterior end at the bottom. Arrowhead indicates a large pericardial edema; BA, bulbus arteriosus; A, atrium; V, ventricle. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
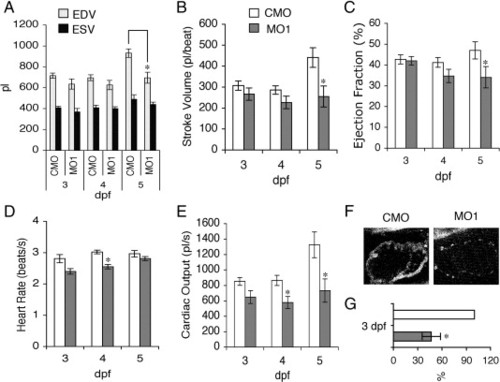
Reduction of zLrrc10 expression causes the defects in heart function. (A) Zebrafish embryos were injected with MO1 or CMO as indicated. To determine EDV and ESV, time-lapse recording was used to follow ventricular movement from a lateral view in embryos at 3–5 dpf. (B) Stroke volume was calculated by subtracting ESV from EDV. (C) Ejection fraction (%) = (EDV - ESV) / EDV × 100. (D) Heart rate was calculated from the number of frames captured during three consecutive, complete ventricular contractions in the time-lapse recordings. (E) Cardiac output was calculated as the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Values are mean ± standard error of the mean with n = 10. An asterisk indicates a significant difference in values between the morphants and control at p < 0.05. (F) Representative fluorescence intensity images of the embryonic hearts are shown in vivo in lateral views with the head to the right using multiphoton microscopy. All images of the control and morphant embryos were obtained at 3 dpf under identical experimental conditions at 780 nm excitation. (G) Relative amounts of NADH were calculated when the control value was set at 100%. n = 4. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
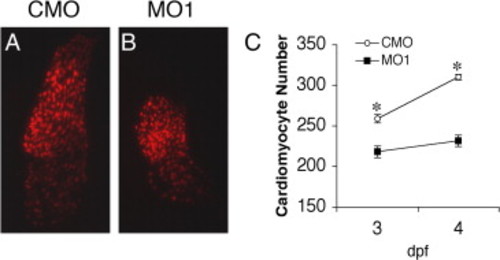
Knockdown of zLrrc10 causes a decrease in the number of cardiac myocytes in developing zebrafish embryos. Transgenic zebrafish embryos expressing RFP in the cardiomyocyte nuclei (cmlc2::dsRed2-nuc) were injected with CMO or MO1. At the indicated time points, fluorescence images were captured, and cells were counted in at least ten hearts per group. Embryos were grown in the presence of 0.003% phenylthiourea from 1 dpf to inhibit pigmentation, which is effective until 4 dpf. (A, B) Representative epifluorescence images of the CMO and MO1 injected cmlc2::dsRed2-nuc transgenic zebrafish hearts at 3 dpf. (C) The number of cardiomyocytes per heart in CMO and MO1 injected embryos. Values represent means ± SEM. *p < 0.01. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The expression levels of anf and cmlc2 were altered in the zlrrc10 morphants. (A) CMO (a, c, e, g, i and k) and MO1 (b, d, f, h, j and l) injected zebrafish embryos at 2 dpf were subjected to whole-mount in situ hybridization using digoxigenin labeled anf (a–d) and cmlc2 (e–h) antisense riboprobes. Images of whole-mount immunostaining using MF20 antibody are shown in k and l. i and j are the same fields as k and l, respectively. c, d, g and h are ventral views and others are lateral views, all with anterior to the left. Note the marked increase in anf expression in the zlrrc10 morphant (b and d) but the reduction of cmlc2 expression in the morphant (f and h). A ventral view of the morphant clearly shows the small ventricle and a looping defect (h). (B) For quantitative analyses of gene expression, RT-PCR was performed on anf and cmlc2. β-actin was used as a control. |

Unillustrated author statements |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 308(2), Kim, K.H., Antkiewicz, D.S., Yan, L., Eliceir, K.W., Heideman, W., Peterson, R.E., and Lee, Y., Lrrc10 is required for early heart development and function in zebrafish, 494-506, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.