Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070810-5
- Publication
- Zhang et al., 2007 - SCL-GFP transgenic zebrafish: In vivo imaging of blood and endothelial development and identification of the initial site of definitive hematopoiesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
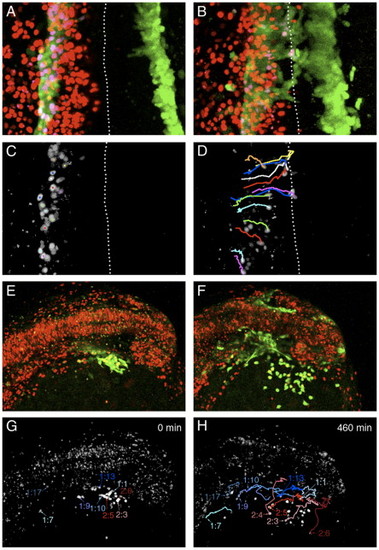
Migration of blood and endothelial precursors. Projections of confocal images from timelapse experiments performed on scl-PAC-GFP transgenic embryos scatter labeled with nuclear-localized H2B-mRFP1 fusion. (A–D) Migration of blood and endothelial precursors from the PLM to the trunk midline. Dorsal view of trunk, anterior to top, dotted line indicates embryonic midline. 3-h Timelapse, 12-min intervals. (A) Projection of GFP and RFP expression at the start of the timelapse (11 somites, 14.5 hpf). The GFP cells are in the PLM. (B) Projection of GFP and RFP expression at the end of the 3-h timelapse (16 somites). GFP expression has begun to reach the midline in the anterior part of the trunk. (C) Colocalization of GFP and RFP expression identifies the nuclei of a subset of the GFP-expressing cells. (Image processed using the ‘RG2B colocalization’ plug-in for ImageJ). (D) The positions of these nuclei at the end of the timelapse are shown, along with the paths they took during their migration. Several of the cells have reached the midline. It is generally the case that the more rostral cells migrate first. However, the migration of the cells is not completely synchronous, and the paths of some nuclei cross. For example, the most rostral cell tracked (orange path) migrates later than cells immediately posterior to it, and crosses their paths. This implies that the cells are migrating independently rather than moving as a tissue en masse. (E–H) Migration of cells from the ALM domain of scl expression to form the head vasculature and yolk sac macrophages. Dorso-lateral view of head, anterior to the right. 460-min timelapse, 10-min intervals. (E) Projection of GFP and RFP expression at the start of the timelapse (13 somites, 15.5 hpf). The GFP-expressing domain is lateral to the midbrain and ventral to the mid- and hindbrain. (F) Projection of GFP and RFP expression at the end of the timelapse (approximately 20 somites). Cells were identified as macrophages or angioblasts by position, shape and arrangement relative to other cells. The ventral GFP-expressing cells are primitive macrophages that have migrated out onto the yolk sac, while the remainder are forming the head vasculature. (G) Colocalization of GFP and nuclear RFP at the start of the timelapse. Selected nuclei are indicated. Those that gave rise to angioblasts are labeled in shades of blue, and those that gave rise to macrophages are labeled in shades of red. (H) Positions of these nuclei at the end of the timelapse, together with the paths they followed. In this experiment, angioblasts were found in the positions of the lateral aorta (1:7, 1:9, 1:10), primordial hindbrain channel (1:17), primordial midbrain channel (1:13) and optic vein (1:1). The paths taken by five cells that gave rise to macrophages are also shown. In general, more posterior and medial cells gave rise to angioblasts while more anterior and lateral cells formed macrophages. However, occasional antero-lateral cells become angioblasts (e.g., 1:1) and some macrophages emerge from more medial positions (e.g., 2.4). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 307(2), Zhang, X.Y., and Rodaway, A.R., SCL-GFP transgenic zebrafish: In vivo imaging of blood and endothelial development and identification of the initial site of definitive hematopoiesis, 179-194, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.