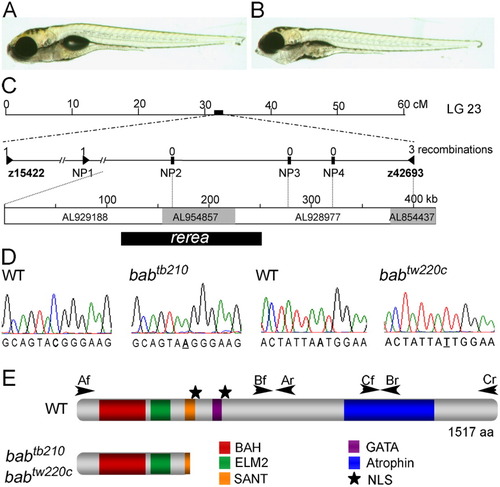
The bab phenotype is caused by a disruption in rerea. A,B: The wild-type (WT, A) and bab (B) larvae at 5 days postfertilization (dpf) are shown in lateral view. Ventral distension of the pharyngeal area in bab is caused by the inverted second arch cartilage. C: The bab locus is at approximately 32 cM on linkage group 23. Expanded view of the genetic map shows the number of recombinations in 2,094 alleles above the marker name. The genomic contigs that span the completely linked region, their Genbank accession numbers, and the position of rerea are shown below. D: Sequence chromatographs of both the babtb210 and babtw220c in comparison with wild-type sequence are shown with the mutation underlined. E: The REREa schematic displays the positions of identified protein domains with colored boxes and nuclear localization signals (NLS) with stars. Arrowheads mark the location and direction of primers used to amplify cDNA. Nonsense mutations in both alleles of bab truncate REREa in the SANT domain.
|

