Fig. S1
|
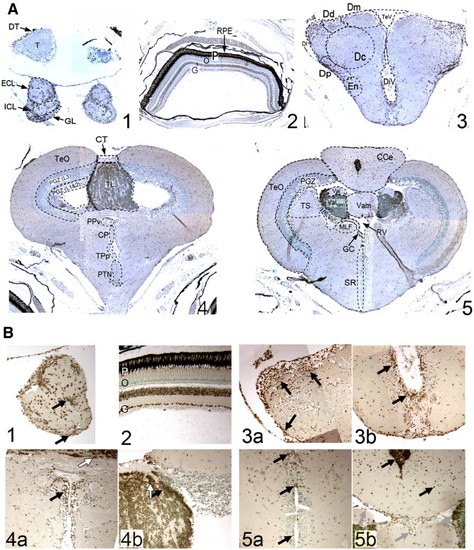
Immunohistochemical staining of coronal brain sections of adult zebrafish brains shows pCREB+ cells are localized within discrete regions in the olfactory bulb (OB; A-i and B-i), retina (A-ii and B-ii), anterior forebrain (telencephalon; A-iii and B-iii), midbrain (mesencephalon/diencephalon A-iv and B-iv) and hindbrain (cerebellum/ rhombencephalon; A-v and B-v; Magnification A1–5: × 10 and B1–5: × 40). Within the OB (A-i and B-i), pCREB+ cells are observed throughout the layers, as seen in sagittal sections, with a strong concentration at the junction of the ECL and ICL (Bi; white arrow). Within the neurally-derived layers of the retina (A-ii and B-ii), strong immunoreactivity for pCREB is observed in the ganglion cell layer (G), and most cells of the inner nuclear layer (I). As in higher vertebrates, no pCREB+ cells are visible in either the outer nuclear layer (O) or the nuclei of the rod and cone photoreceptors (P). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 307(1), Dworkin, S., Heath, J.K., Dejong-Curtain, T.A., Hogan, B.M., Lieschke, G.J., Malaterre, J., Ramsay, R.G., and Mantamadiotis, T., CREB activity modulates neural cell proliferation, midbrain-hindbrain organization and patterning in zebrafish, 127-141, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.