- Title
-
Variants in NR6A1 cause a novel oculo vertebral renal syndrome
- Authors
- Neelathi, U.M., Ullah, E., George, A., Maftei, M.I., Boobalan, E., Sanchez-Mendoza, D., Adams, C., McGaughey, D., Sergeev, Y.V., Ai Rawi, R., Naik, A., Bender, C., Maumenee, I.H., Michaelides, M., Tan, T.G., Lin, S., Villasmil, R., Blain, D., Hufnagel, R.B., Arno, G., Young, R.M., Guan, B., Brooks, B.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
Phenotypes associated with variants in |
|
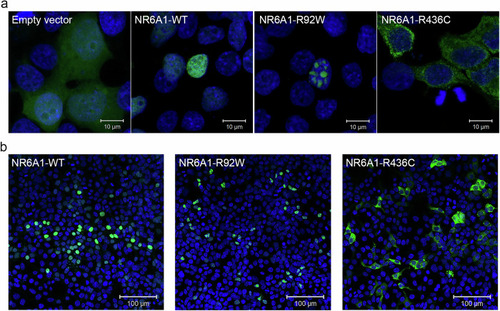
Subcellular localization of wild-type (WT) and mutant forms of NR6A1. NR6A1 variant localization pattern was studied by overexpression in HEK293 cells and representative high magnification (63X) images are shown from three different trials ( |
|
|
|
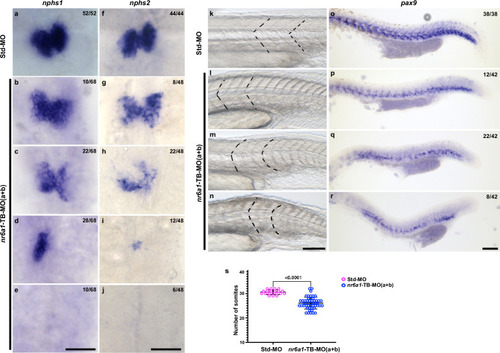
Expression pattern of EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Rescue of Controls ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
At 48 hpf, control embryos demonstrate bilateral expression of |